In its continued efforts to tame inflation, the Federal Reserve increased interest rates ¼ point last week, the tenth consecutive increase in just over a year. The cumulative increase is 500bps since March 2022, bringing the Fed Funds rate to 5.00%-5.25%, which is the highest since 2007. While inflation is still above the Fed’s target rate of 2%, they indicated a pause in rate increases. The labor market continues to be strong with April unemployment down to 3.4%, matching
the low of January which is the lowest unemployment since 1969.
Despite all the efforts by the Fed to have a soft landing, the economy could be upended if Congress does not increase the debt ceiling soon. With inflation slowing, and the labor market strong, a soft landing is possible. Treasury Secretary Yellen said the U.S. could default on debt as early as June 1st. If the U.S. defaults on outstanding debt, many forecast disastrous impacts to the world economy.
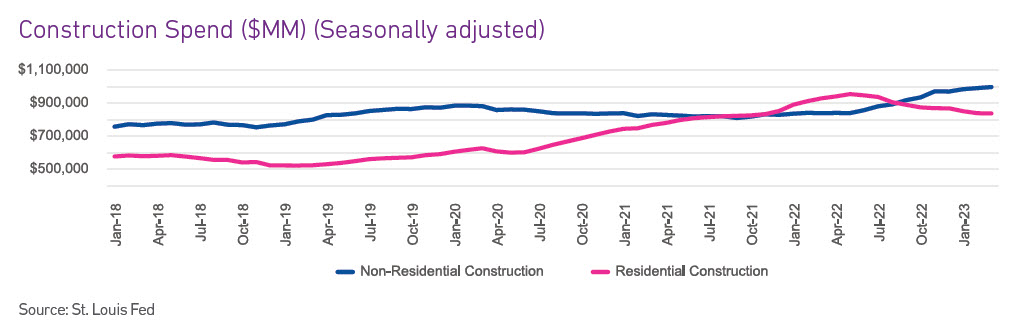
and non-residential sectors.
The construction industry is one of the few industries that saw a boom throughout the pandemic. Even though over the past few months both residential and non-residential experienced a decline in construction starts and construction spend, the volumes remain above pre-pandemic levels. High construction demand is being met with the formation of many new construction companies. New construction companies are seeking credit at a higher rate, but delinquencies in the construction industry are increasing. Higher risk and higher interest rates are causing commercial lending to tighten, and construction companies are seeing fewer loan originations and smaller loans/lines of credit.
What I am watching:
The non-residential construction industry is expected to see steady growth in 2023 due to project backlogs but could slow in 2024. Due to higher mortgage rates, the residential construction industry is expected to see a significant decline in housing starts through 2023 with the sector stabilizing in 2024. Aside from the immediate key drivers of interest rates and cost of capital, other areas of focus will be on the labor force and the demand for skilled vs. non-skilled labor. The number of skilled workers is decreasing yet the demand for skilled labor is increasing. The construction industry will have to attract the necessary talent to support the growth.
Operational changes in the construction industry will be a driving factor. The construction industry is seeing a shift toward technology in all aspects of construction. Utilization of robotics is increasing which could replace portions of the workforce. Smart Cities, Smart Homes, Green Building are all trending which will materially change construction projects. The Construction Industry is experiencing a noticeable shift and companies will continue to adapt to keep up with demand.
