eCommerce and Retail
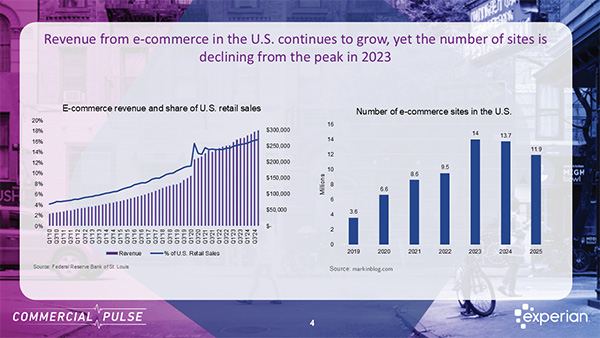
Experian Commercial Pulse Report reveals decline in total number of ecommerce businesses, strong revenue, and fewer credit inquiries.
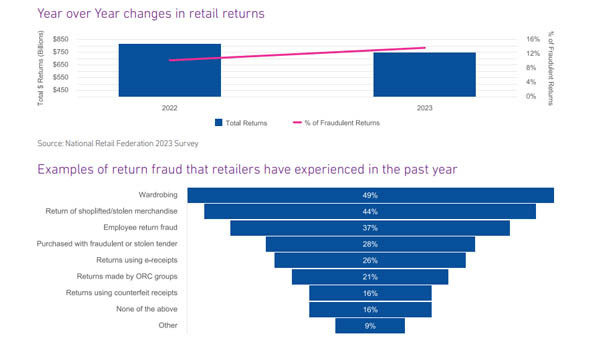
Retail sales reached a 4-year high of over $615B in December 2023 with yearly retail sales growing 4.6%. At the same time, lenders are tightening credit and businesses within the retail sector are showing signs of stress with higher late-stage delinquency rates and falling commercial credit scores. We see retailers seeking commercial credit less often, new originations slowing and lower lines over the past several months. As retail sales continue to rise so does the proportion of online retail sales. Online sales peaked during the COVID-19 pandemic and fell slightly once the lockdowns were lifted. Online retail sales remain approximately 56% higher than pre-pandemic levels and are trending up and may soon exceed 2020 levels. Growth in online retail sales has led to growth in retail returns. Retail returns peaked in 2022 at over $800MM and over 16% of total retail sales. Prior to 2021, retail returns as a percentage of retail sales averaged 8.9%, since 2021 that rate has grown to 14.6%. As returns increase so do fraudulent returns. Retailers have implemented strategies and solutions to address retail returns which resulted in a decrease in return dollars between 2022 and 2023 yet the percentage of returns that were fraudulent increased from 10.2% to 13.7% or over $100B. Increases in both legitimate and fraudulent returns are prompting retailers to identity solutions and operational strategies to slow growth across all returns. What I am watching: The U.S. economy expanded 3.3% in Q4 2023, and 2023 real GDP increased 2.5% over 2022. Strong consumer spending fueled the economy. Multiple sources are expecting The Federal Reserve to cut interest rates up to six times in 2024 with the rate cuts beginning in Q2 2024 and continuing into 2025. Lower interest rates likely means that consumer spending will continue at an elevated rate. As spending continues to increase, specifically in the retail sector, the need for commercial credit could continue to slow as cash-flows satisfy operational capital requirements. Cash on hand should begin to satisfy outstanding delinquencies, improving commercial credit scores resulting in improved access to commercial credit.
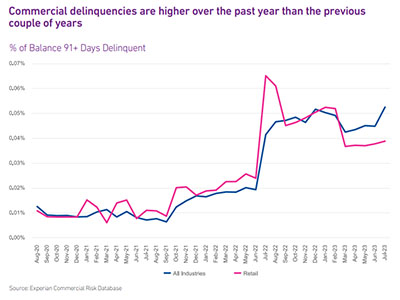
The labor market remains robust with low unemployment (3.8%) and 366K new jobs created in September. Job openings in the U.S. were 9.6MM as of the end of August, an increase of 690K or 5.8% since July. Retail sales in August had a month-over month increase for the fifth consecutive month. As we head into the holiday shopping season, despite headlines of large retailers struggling, the retail industry appears poised for success. It is likely that those retail businesses that survived the difficulties of the pandemic are the most financially sound and are driving the statistics. Over the past year, retailers are seeking less credit and taking on less debt than the previous few years. Despite inflation, consumers are still spending, and retailers are benefitting. Commercial delinquencies have been increasing over the past year. Delinquencies within the retail sector were trending above overall commercial delinquencies until just a few months ago when retailers exhibited lower rates than overall. These are all positive signs heading into the holiday shopping season which tends to make or break a retailer’s year. The September labor report was stronger than expected. Unemployment remained low at 3.8% and 366K new jobs were created which was the highest amount since January. In addition, the jobs created in July and August were revised upward significantly. What I am watching: With the labor market still tight, it will be interesting to see if the retail sector will be able to staff accordingly to support the holiday crunch. If staffing is difficult, retail stores may struggle to keep up with demand. Now that the student loan moratorium has ended, it will be important to monitor the impact to consumer spend. The increased expense of the student loan monthly payments will likely leave individuals with less discretionary income to spend on retail purchases. In addition, business owners who have student loans will have less money to invest in their business
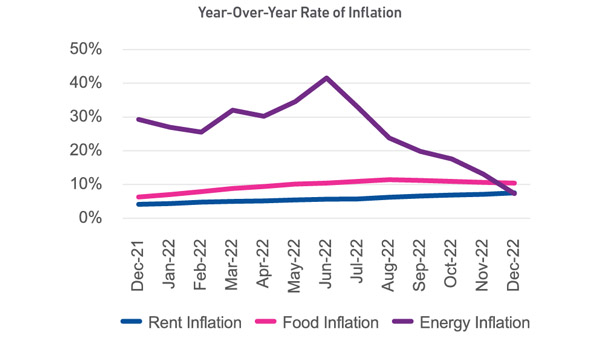
So far, the economy has been extremely resilient, with Q4 GDP coming in above expectations at 2.9%, inflation cooling, supply chain issues easing, and unemployment remaining low.

Heading into the holiday season, we'll see if consumers continue to spend at high levels, or if higher prices, higher interest rates and lower savings create a drag on sales.

As business delinquencies rise in response to COVID-19, credit departments are becoming increasingly challenged. In our August 13th Sip and Solve webinar, John Krickus and Andrew Moore will be on hand to share some strategies for maximizing receivables amid rising delinquencies. Managing receivables has never been more important or more challenging. Traditional approaches may no longer apply. In this 15-minute Sip and Solve session, we discuss some solutions for effectively and efficiently handling the increase in receivables many companies are facing. After watching this talk you will learn three key takeaways: Prioritizing receivable management in today's environment Analytic tools for managing receivables Flexing receivables strategies to meet your company's priorities Click to view full slides and transcripts from this session.

In a favorable economic climate, business resilience is often treated as an afterthought. Success is measured in rapid growth and leaps of progress, while failure is little more than a tempering of that expansion. It’s only when things slow down - like during a global pandemic - that companies are forced to take stock of the ground they stand on. As the economy slows to a crawl and entire industries feel the squeeze, business resilience will determine which organizations make it through to the other side. Whether you’re on the supply side or the demand side, chances are your organization is being tested right now. Here are some practical strategies to stay resilient in the time of Covid-19. Gerard Smith, President of Global Risk Management Solutions (GRMS), works with companies who are either on-boarding new suppliers or evaluating current suppliers. When the Covid-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains in most industries, many of these companies started scrambling to find replacement suppliers. Finding a reliable supplier is always a challenge, but it’s even more difficult during a global pandemic and economic crisis. The best practice here is still to vet new suppliers carefully. Smith’s company creates a risk assessment program for Experian clients that analyzes 50 different financial and legal components, including the following: If they’re on the OFAC sanctions list If they’re financially stable If they actually have the certifications they claim to have If they have insurance If they’ve received negative press Many companies fail to do their due diligence when it comes to suppliers, especially if they’re trying to fulfill orders quickly. More often than not, this leads to bigger problems down the line. If you hire a supplier that’s hemorrhaging money, for instance, they may file for bankruptcy right after you pay them for a major shipment. Companies that use GRMS will be notified regularly if a supplier’s financial or legal status changes. If a supplier cancels their insurance coverage, for example, that could indicate financial struggles. Staying abreast of information like this allows businesses to be proactive with suppliers and avoid being blindsided. Make Sure Clients Are Financially Healthy On the flip side of the buyer-supplier relationship, suppliers are now being asked to extend due dates. Deciding how to comply with these requests can be tricky. Most want to be understanding and reasonable, but there is often legitimate concern over whether they’ll receive payment. Brodie Oldham, Senior Director of Analytic Consultancy for Experian, said Experian offers several services for suppliers who need to gauge how reliable their customers are in this moment. Experian has a special Covid-19 risk index that suppliers can overlay on top of existing credit models. This tool can help determine whether or not a client is in an unstable financial position. If the company operates in a highly impacted part of the country or industry, the supplier can use that information to change the terms. For example, they can sell fewer items to minimize the risk of an unpaid invoice. Experian also monitors credit utilization for business credit cards and other lines of credit. If a company’s credit utilization surpasses a certain threshold, they can alert the supplier who can halt future shipments until the utilization decreases. Find Faster Ways to Evaluate Creditworthiness Many suppliers depend on a company’s credit information to determine its reliability as a buyer. Likewise, credit bureaus are being forced to reevaluate their models in response to the changing business landscape brought on by Covid-19. Enter the agile credit function. The term agile has traditionally been used in the context of software development to describe an iterative approach where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams. It allows companies to adapt to new requests quickly and improve time-to-market. Agile is all about being nimble and responsive - something credit bureaus are prioritizing in today’s uncertain economy. Agile credit means finding new, faster ways of evaluating customers and determining their ability to pay, in a time when that information can change daily. “When everything shut down in March, credit people got thrown for a loop,” said Dan Meder, Vice President of Consulting, Product Marketing and Alliances for Experian Business Information Services. “They needed a way to manage that change very quickly.” That’s where having an agile credit approach comes in. “It’s about using agile principles in your credit function to respond more quickly to changing market needs,” Meder said. Using an agile credit system helps suppliers decide what kind of terms to offer their customers. Many companies are asking suppliers to extend their terms and due dates, often switching from net-30 to net-60. Suppliers then have to decide if they can trust these companies to repay them within that longer time frame, Meder said. If companies in this position use an agile credit function, they can be more responsive and confident in the terms they set out because they’re basing their credit policies on the current state of their customer environment. This requires operating with the latest possible information on how current economic conditions are affecting their customers. Meder said that making credit function more agile requires direction from the head of the credit department and other members of that department. They can also utilize software programmers if the automatic process needs to be updated or any outside consultants for specific analytical expertise. “The idea is to bring together a team of people with direct involvement in managing the credit function to assess how best to manage the customer experience given the current state of the customer environment,” he said. “This includes setting policies around risk assessment as well as credit terms and collection processes.” Meder said companies should have technology that allows them to tinker with their credit function so they can make changes quickly. “This is especially true in a fast-changing or uncertain environment such as what we are seeing with COVID-19 and the uncertain effect it is having on our economy’s future,” he said. “In fact, it is turbulent times such as these where being “agile” is most important since the credit department needs to be able to alter course quickly if the customer environment changes for better or for worse.” Consider Being Flexible With Clients While delayed payments from clients is upsetting, avoid taking your current client relationships for granted. While a more stringent approach from suppliers is understandable right now, Meder cautions companies to remember that the pandemic will end at some point. At that time, companies will remember which suppliers were flexible about payments, due dates and terms - and which companies weren’t. “If you weren’t good to them while they were struggling, they’re going to forget about you when things turn around,” Meder said. To find out how fine-tuning your company’s credit function can help it weather the current economic crisis, reach out to your Experian representative.

When a new customer wants to establish credit terms with you, the first thing they’re asked to do is fill out your credit application. When you hand over a paper application, did you know you could be negatively impacting your revenue or creating a poor customer experience? Some companies don’t. More than likely, your customer has filled out at least one digital application in the past. The initial perception your application says about your company is that you’re out of step with technology — which may lead them to wonder where else you may be lagging behind. Digital applications provide a simplicity factor, and by not offering one, your credit approval process is perceived to be more difficult, leaving the customer with more work to do —spending extra time writing their information by hand and returning the application — either by email, fax, or in person. Because many companies have already moved to a digital application, your pen-and-paper process sticks out to the customer — and not in a good way. Not to mention, manually processing a paper application takes longer — often much longer — than a digital application. This means customers leave without a credit approval, giving them time to change their mind about their purchase or find a better deal — meaning you just lost a new sale. And even if they still choose to work with you, their relationship with your company starts out with a less-than-amazing customer experience. After the paper application is completed, the workflow process is often time-consuming, error-prone, and cumbersome. The time involved also means that your company waits longer to receive revenue from the sale. By using a manual process, your team spends hours on processing and decisions that could be better spent directly servicing customers or working on other initiatives to grow business. DecisionIQ from Experian automates consistent real-time decisions, streamlining your entire process from applications to onboarding.

For lenders, alternative data can be the factor in edging out your competitors, especially when better decisions are needed to compete for emerging businesses and startups. Both startups and emerging businesses may represent a good growth opportunity, but they may also be high risk. The challenge? Businesses with thin credit profiles can be difficult to score. Social Media Insight TM provides lenders with another layer of data that can help you better assess the direction of these businesses, score them more accurately and open new growth opportunities. After all, nobody likes to leave money on the table. For emerging businesses who have a thin credit profile but have a strong social media reputation, Social Media Insight can be a factor in gaining access to credit and resources they deserve. Social Media Insight enables you to see the activity, trends and sentiment on a business, over time. In our Experian DataLab tests, we improved overall model performance by 12 percent and new and emerging businesses by 91 percent, boosting predictive performance over traditional data sets. Social Media Insight is directly sourced data providing you with over 70 attributes including trends and sentiment along with descriptive attributes. This powerful data enables you to more accurately score or assess new and emerging business as well as long established accounts. Want to learn more? Watch our on-demand webinar or contact your Experian representative today.
