Topics

Discover how business identity theft threatens B2B firms and learn effective strategies to protect your business and clients. Stay informed and secure.

Experian Summer Beyond The Trends Report Now Available We are excited to announce the release of the Summer 2024 Beyond the Trends report. The report offers a unique view of the small business economy based on what we see in the data. With up-to-date information on over 33 million active businesses and how they perform from a credit standpoint, in this report, Experian shares insights and commentary on how economic conditions, public policy, and other factors might shape future small business performance. Here's our V.P. of Commercial Data Science, Brodie Oldham with his quick take. Overall, the sentiment among small businesses regarding growth is cautiously optimistic. Optimism Despite Challenges There is a general sense of optimism reflected in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Small Business Index, which has risen to 69.5. Additionally, 73% of small businesses expect higher revenues, and 46% plan to increase investments, indicating positive growth expectations despite facing persistent challenges such as inflation, worker shortages, and rising operational costs. Government Support and Initiatives Various government programs and initiatives are bolstering small business growth by improving access to capital and providing targeted support. These initiatives include the Investing in America Small Business Hub, expansion of Women’s Business Centers, and improvements in the 7(a) and 504 Loan Programs, all aimed at facilitating job creation, growth, and sustainability. Technological Adaptation The adoption of AI and other advanced technologies by small businesses is enhancing operational efficiency and cutting costs. A significant increase in the use of AI-driven systems, such as CRM and automated inventory management, indicates that small businesses are leveraging technology to drive growth and stay competitive. Resilience Amid Economic Pressures Despite facing economic headwinds like tighter credit conditions due to higher interest rates and ongoing supply chain disruptions, small businesses have shown resilience. They continue to navigate these challenges by employing innovative strategies and adapting to the evolving economic landscape. Download your copy of the latest report and check out more insights on small businesses on our Commercial Insights Hub where you can subscribe to updates. Download Beyond The Trends Report Commercial Insights Hub

Explore how API integration transforms business efficiency, enabling seamless data management, automation, and advanced client segmentation for growth and risk management.

Explore instant decisioning in business automation, an approach to streamline credit decisions integrating data and automating processes.

Explore how batch append credit scores revolutionize risk management and efficiency in financial services, with insights from Experian's Erikk Kropp.

Data is central to modernizing the credit approval process. We discuss useful formats beyond traditional business credit reports and scores.

We're kicking off a series of posts about the path to modernization framework featuring Sr. Product Manager, Erikk Kropp.
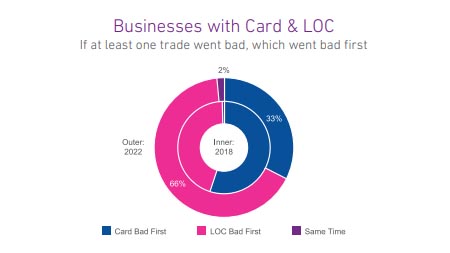
Since January 2021, a seasonally adjusted average of 444K new businesses opened each month, 52% higher than the pre-pandemic 2018-2019 monthly average. In light of the influx of new businesses, and in a higher-interest rate environment, the goal of this week’s analysis was to evaluate if commercial credit usage and payments by product shifted pre- and post-pandemic. Businesses with two different trade types were evaluated as of 2018 (prepandemic) and 2022 (post-pandemic). The two-trade-type combinations observed were Card + OECL (open ended credit line), Card +Term Loan, Card Lease, and Card + LOC (line of credit). Despite more younger businesses entering the market and lenders tightening credit policies over the past two years, businesses with two-trade types had higher lines/loans post-pandemic. Delinquencies also increased post-pandemic for all the two-trade type combinations except businesses with a Card & OECL. Commercial Cards are the most prevalent type of credit for businesses. As businesses grow, they seek additional credit for business needs such as expansion, new facilities, and acquisitions. When businesses seek additional credit, it is most often in the form of commercial loans, leases and credit lines which compared to cards, generally provide higher levels of funding, longer terms and higher monthly fixed payments. For businesses that had two types of accounts, including a commercial card with another commercial credit product, the commercial card stayed current longer and more often the non-card product went delinquent first. Businesses rely on commercial cards for day-to-day operating expenses and lower dollar financing needs. Furthermore, commercial card balances are significantly lower than any of the other commercial trade types allowing for a lower monthly minimum payment to keep the card in good standing. What I am watching: Federal Reserve Chairman Powell stated in last week’s Congressional hearings that the Fed will act slowly and cautiously in terms of cutting interest rates. With inflation declining but still persistent and the labor market still robust, rate cuts may not occur until the second half of the year. Download Report Download the latest version of the Commercial Pulse Report here. Better yet, subscribe so you'll get it in your inbox every time it releases, or once a month as you choose.

Experian's Kyle Matthies provides a roundup of international credit report usage statistics showing which regions are surging or declining.
