Employers today have an ever-growing list of obligations to meet to keep their companies in good standing and with a focus on compliance to avoid Form I-9 violations and fines.
The purpose of Form I-9 is to verify the identity and employment authorization of individuals hired for employment in the United States. As part of the Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986, employers bear the burden of inspecting documents provided by new employees to confirm lawful employment authorization and must properly maintain an I-9 record for each of them.
Failing to meet this requirement puts employers at risk of severe Form I-9 penalties that could negatively affect their company’s bottom line. Therefore, it is critical to take every possible precaution to avoid Form I-9 fines, especially in light of the recent increase in Form I-9 penalties.
Increased Form I-9 Violation Fines for Mistakes
In October 2021, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) released increased fines for Form I-9 civil penalties to account for annual inflation. The new fines are effective for Form I-9 penalties assessed after October 18, 2021, for associated violations that occurred after November 02, 2015.
In order to avoid Form I-9 fines, employers need to be aware of the recent adjustments:
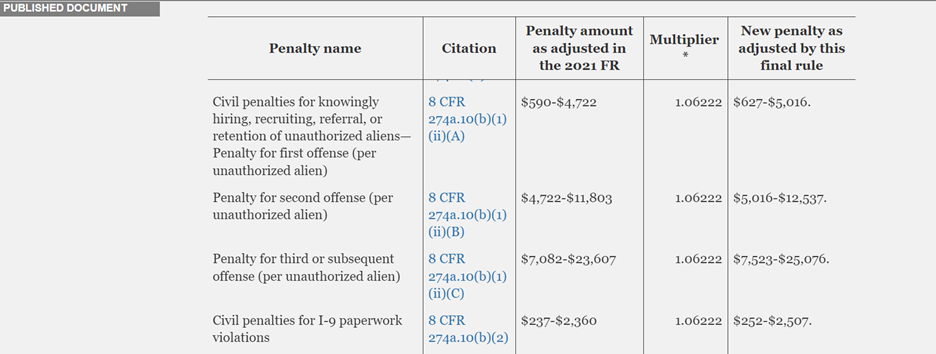
- The minimum fine per violation for substantive paperwork or uncorrected technical violations was increased from $237 to $252;
- The maximum fine per violation for substantive paperwork or uncorrected technical violations was increased from $2,360 to $2,507;
- First offense fines were increased from $583-$4,667 to $627-$5,016;
- Second offense fines was increased from $4,667-$11,665 to $5,016-$12,537; and
- Third or subsequent offense fines were increased from $6,999-$23,331 to $7,523-$25,076.
Taking into account that any mistakes made in filling out and filing Form I-9 can be even more costly than before, employers need to adhere to the necessary rules and procedures. To avoid Form I-9 fines, they should regularly assess their company’s hiring processes, retention and storage policies, fully understand the types of Form I-9 violations and lawfully correct any errors, if the need arises.
Common I-9 Mistakes
The best way for employers to minimize the risks, prevent errors and identify areas for improvement is to establish a comprehensive and effective Form I-9 compliance. To do this properly and avoid Form I-9 fines, it is necessary to understand common I-9 mistakes.
Errors and omissions discovered during a Form I-9 inspection can be classified as either technical or substantive violations.
Examples of technical violations include:
- Failure to ensure an individual provides their employee name, address, or birth date in Section 1;
- Failure to ensure the individual dates Section 1 at the time employment begins;
- Failure of the form’s preparer or translator to print their name, address, signature or date in the preparer’s certification box;
- Failure to provide the document title, identification numbers and expiration dates of proper List A documents or proper List B and List C documents in Section 2 or 3. This is necessary only if legible copies of the documents are retained with the forms and presented at the I-9 inspections;
- Failure to provide the title, business name and business address in Section 2; or
- Failure to provide the date of rehire in Section 3.
Examples of substantive violations include:
- Failure to timely prepare Form I-9;
- Failure to timely present Form I-9;
- Failure to prepare Form I-9 for an employee;
- Failure to complete Section 2 within 3 business days of hire;
- Failure to reverify employment authorization in a timely manner in Section 3, when applicable;
- Failure to date Section 2 of the Form I-9;
- Failure to review and verify a proper List A document or proper List B and List C documents in Section 2 or 3;
- Failure by the employer to sign the attestation in Section 2 of Form I-9;
- Failure by the employer to sign the attestation in Section 3 when reverification is required;
- Completing a false Section 2 attestation when the certifier examines the documents outside the presence of the employee presenting them;
- Failure by the employee to sign Section 1; or
- Failure to correct technical errors within the allotted window after being served a Notice of Technical or Procedural Failures letter by ICE.
How to take Proactive Measures to Avoid Form I-9 Fines
With the DHS and US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) extending some of the COVID-19 policies, employers may have a false sense of relaxation when it comes to Form I-9 compliance. However, the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) is still conducting worksite enforcement audits and if employers fail to complete, retain or make Forms I-9 available for inspection, the punishments imposed can result in significant penalties. Therefore, to avoid Form I-9 fines, employers are encouraged to take proactive measures, develop proper procedures and perform regular self-audits. On the other hand, employers who fail to do this or to properly train and supervise the preparation and maintenance of Forms I-9 expose themselves to sizable risks by making common I-9 mistakes.
While some errors may be corrected, employers can avoid Form I-9 fines and significant expenses by developing internal procedures to ensure that every form is properly completed, verified, maintained and readily accessible. To simplify this and transform hiring compliance into a highly efficient and reliable operation, they can automate Form I-9 administration, convert paper documents to compliant electronic forms, filter outdated files, remediate errors, and avoid costly Form I-9 penalties. As a result, employers replace the risks and expenses of outdated, obsolete I-9 processes in favor of smarter, faster and more reliable Form I-9 management and compliance.


