Financial Services

Direct mail is dead. It’s so 90s. Digital is the way to reach consumers. Marketers have heard this time and again, and many have shifted their campaign focus to the digital space. But as our lives become more and more consumed by digital media, consumers are giving less time and attention to the digital messages they receive. The average lifespan of an email is now just two seconds and brand recall directly after seeing a digital ad is just 44%, compared to direct mail which has a brand recall of 75%. Further research shows direct mail marketing is one of the most effective tools for customer acquisition and loan growth. The current Data & Marketing Association (DMA) response rate report reveals the direct mail response rates for 2016 were at the highest levels since 2003. Additionally, while mailing volume has trended down since October 2016, response rates have trended up, and reached 0.68% in March 2017, up from 0.56% in October 2016. Using data and insights to tailor a direct mail campaign can yield big results. Here are some attention-grabbing tips: Identify Your Target Market: Before developing your offer and messaging strategy, begin with the customer profile you are trying to attract. Propensity models and estimated interest rates are great tools for identifying consumers who are more likely to respond to an offer. Adding them as an additional filter to a credit-qualified population can help increase response rates. Verify your Mailing List: Experian’s address verification software validates the accuracy and completeness of a physical address, flags inaccuracies, and corrects errors before they can negatively impact your campaign. Personalize the Offer: Consumers are more likely to open offers that are personalized, and appeal to their life stage, organizational affiliations or interests. Experian’s Mosiac profile report is a simple, inexpensive way to gather data-based insight into the lifestyle and demographics of your audience. Time the Offer: Timing your campaign with peak market demand is key. For example, personal loan demand is highest in the first quarter after the holidays, while student loans demand peaks in the Spring. Direct mail can help overcome digital fatigue that many consumers are experiencing, and when done right, it’s the printed piece that helps marketers boost response rates.
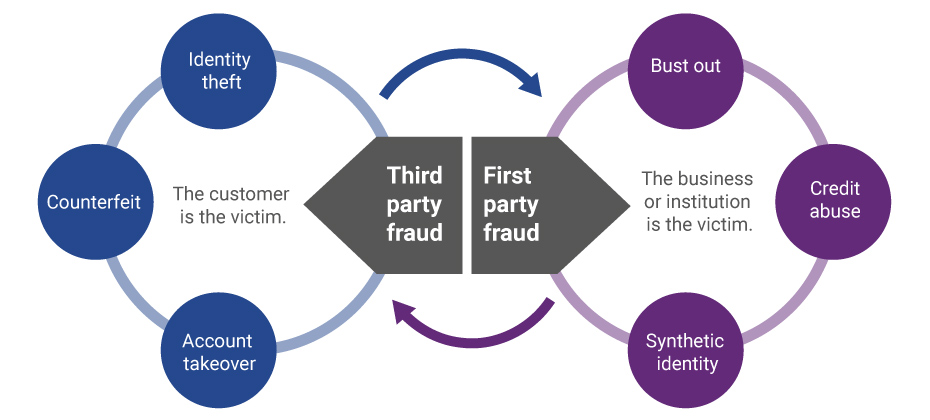
Evolution of first-party fraud to third Third-party and first-party schemes are now interchangeable, and traditional fraud detection practices are less effective in fighting these evolving fraud types. Fighting this shifting problem is a challenge, but it isn’t impossible. To start, incorporate new and more robust data into your identity verification program and provide consistent fraud classification and tagging. Learn more>

It should come as no surprise that the process of trying to collect on past-due accounts has been evolving. We’ve seen the migration from traditional mail and outbound calls, to offering an electronic payment portal, to digital collections and virtual negotiators. Being able to get consumers who have past-due debt on the phone to discuss payments is almost impossible. In fact, a recent informal survey divulged a success rate of a 15% contact rate to be considered the best by several first-party collectors; most reported contact rates in the 8%-range. One can only imagine what it must be like for collection agencies and debt buyers. Perhaps, inviting the consumer to establish a non-threatening dialog with an online system can be a better approach? Now that collectors have had time to test virtual collections, we’ve collected some data points. Conversion rates, revisits, and time of day An analysis of several clients found that on average 52% of consumers that visit a digital site will proceed to a payment schedule if the right offer is made. 21% of the visits were outside the core hours of 8 a.m. to 8 p.m., an indication that consumers were taking advantage of the flexibility of reaching out at any time of the day or night to explore their payment and settlement options. The traditional business hours don’t always work. Here is where it really gets interesting, and invites a clear comparison to the traditional phone calls that collectors make trying to get the consumer to commit to a payment plan on the line. Of the consumers that committed to a payment plan, only 56% did it in a single visit. The remaining 44% that committed to payments did so mostly later that day, or on a subsequent day. This strongly suggests they either took time to check their financial status, or perhaps asked a friend or family to help with the payment. In other words, rather than refusing to agree to an instantaneous agreement pressured by a collector, the consumer took time to reflect and decide what was the best course of action to settle the amount due. On a similar note, the attrition rate of “Promises to Pay” were 24% lower using online digital solutions versus the traditional collector phone call. This would be consistent with more time to agree to a payment plan that could be met, rather than weakly agreeing to a collector phone call just to get the collector off the phone. Another possible reason for a lower attrition rate may be that a well-defined digital collection solution can send out reminders to consumers via email or text in advance of the next scheduled payment, so that the consumer can be reminded to have the funds available when the next payment hits their account. For accounts where settlement offers are part of the mix, a higher percentage of balances is being resolved versus the collection floor. In fact, the average payment improvement is 12% over what collectors tend to get on the collections floor. The reason for this significant change is unclear, but the suspicion is that a digital collection solution will negotiate stronger than a collector, who is often moving to the bottom of an acceptable range too soon. What's next? Further assessing the consumer’s needs and capabilities during the negotiation session will undoubtedly be a theme going forward. Logical next steps will include a “behind-the-scenes” look at the consumer’s entire credit picture to help the creditor craft an optimal settlement amount that both the consumer can meet, and at the same time optimizes recovery. Potential impact to credit scores will also come into the picture. Depending on where the consumer and his past-due debt is in the credit lifecycle, being able to reasonably forecast the negative impact of a missed payment can act as an additional argument for making a past-due or delinquent payment now. As more financial institutions test this new virtual approach, we anticipate customer satisfaction and resolutions will continue to climb.
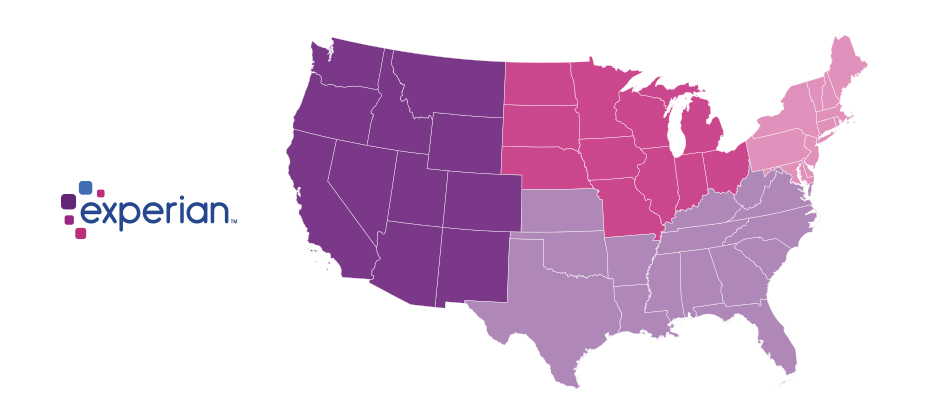
We recently analyzed millions of online transactions from the first half of 2017 to identify fraud attack rates. Here are the top 3 riskiest states for e-commerce billing and shipping fraud for H1 2017: Riskiest states for billing fraud Oregon Delaware Washington, D.C. Riskiest states for shipping fraud Oregon Delaware Florida Fraudsters are extremely creative, motivated and often connected. Protect all points of contact with your customers to prevent this growing type of fraud. Is your state in the top 10?

National Hispanic Heritage Month is observed each year from Sept. 15 to Oct. 15, by celebrating the histories, cultures and contributions of American citizens whose ancestors came from Spain, Mexico, the Caribbean and Central and South America. With one in six U.S. residents being Hispanic, all communities are impacted by the contributions of Hispanics—and now is a great time for financial institutions to reflect upon their largest growth opportunity. What is the best way to reach Hispanic consumers? What are the nuances of the Hispanic market? What are some of the myths FIs have about the Hispanic community? Miriam De Dios Woodward, CEO of Coopera, a Hispanic market strategy firm that helps credit unions reach and serve the Hispanic consumer segment, recently chatted with Experian about serving the Hispanic market. Here she shares her thoughts: Are there special considerations or insights credit unions should know when serving the Hispanic market? It’s very important to understand the Hispanic market is nuanced. There are 22 Spanish-speaking Latin American countries from which prospective Hispanic credit union members may hail. Add to that the fact, many U.S.-born Hispanics think, speak and behave differently than their parents and grandparents. Layer over this the existence of segments like small business owners or Millennials and you can begin to see the complexities involved with targeting and serving a multi-faceted Hispanic market. A smart Hispanic membership growth strategy will be based on segmentation, so credit unions should be willing to invest upfront in good market research. You have to understand what your local Hispanic community really looks like before you can mobilize your teams and leadership around serving them well. Are there particular consumer trends you have seen in the Hispanic community that impact the financial services space? The increasing digitization of financial services is a trend that definitely impacts Hispanic consumers. That’s because Hispanics typically over-index in studies that look at consumer use of connected devices, online banking and social media. A good Hispanic membership growth strategy will take mobile and digital products and services into account and will be tailored to the specific needs of local Hispanic communities. People often assume the Hispanic market is largely centered in states like California, Arizona, Texas and New Mexico. Are you finding that credit unions outside of these southwestern states are discovering they too need to build out a strategy in partnering with this consumer base? Absolutely. Hispanic population growth is happening far beyond so-called “gateway states” like those you mention above. In fact, states such as North Dakota, Kentucky, Louisiana, Delaware and Maryland actually saw the largest Hispanic population growth between 2007 and 2014. Midwestern states, too, are discovering just as many opportunities for engagement with their own growing numbers of Hispanic residents. Iowa and Wisconsin, for instance, each experienced explosive growth rates and now count Hispanics among one of the largest, fastest-growing and youngest groups in their cities. With a comprehensive and strategic approach to Hispanic membership growth, credit unions in unexpected places can become the preferred financial institution for this important segment. That’s because a great number of Hispanics in the U.S. are not tethered to an existing financial relationship. For more on this, check out our recent white paper Hispanic Member Growth Not Just for 'Gateway States' Anymore. What are the biggest myths financial services companies have about the Hispanic community? While there continue to be many misconceptions about the multifaceted Hispanic community, the following three continue to prevail most heavily. Myth: Hispanic consumers are only interested in transaction-based products. Check cashing and remittances are necessary services for many first generation Hispanic segments. At the same time, many of these consumers are interested in long-term relationships. Our own research indicates product penetration increases at a faster rate among Hispanic members as compared to non-Hispanic members when credit unions execute a strategic plan. Myth: The majority of Hispanics are undocumented. This misperception has been somewhat renewed this year with all the political back and forth on the subject of immigration. That’s why it’s so important for credit unions to educate – from the inside out – stakeholders on the facts. Many people do not know, for instance, that of the country's more than 52 million Hispanics, most are native-born Americans, and nearly three in four are U.S. citizens. Myth: The law prevents us from serving immigrants. There are many forms of acceptable government issued identification, such as passports and consular cards that are in full compliance with the Patriot Act and Customer Identification Program rules. In addition, financial institutions can compliantly lend to individuals who have Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers. In fact, the NCUA wants credit unions to serve Hispanic members, including Hispanic immigrants. For more on this, check out the recording of the NCUA hosted panel, “Unique Challenges and Opportunities Serving Hispanic Credit Union Members.” For a credit union seeking to build a relationship with this community, what are your recommendations? Are there particular products or touchpoints they should focus on? Solidifying the right organizational mentality first is an important best practice. Building buy-in, doing the market research, developing a comprehensive strategy based on segmentation and defining what success truly looks like – these are all a part of laying the foundation for success with the Hispanic market. Credit unions should also be smart about talking to and partnering with local organizations that already know – and are trusted by – Hispanic residents. Conducting focus groups with the leaders of these groups and the people they serve can give credit unions a wealth of information about the makeup of their local Hispanic community and the value they might bring to the community.

We use our laptops and mobile phones every day to communicate with our friends, family, and co-workers. But how do software programs communicate with each other? APIs--Application Programming Interfaces--are the hidden backbone of our modern world, allowing software programs to communicate with one another. Behind the scenes of every app and website we use, is a mesh of systems “talking” to each other through a series of APIs. Today, the API economy is quickly changing how the world interacts. Everything from photo sharing, to online shopping, to hailing a cab is happening through APIs. Because of APIs, technical innovation is happening at a faster pace than ever. We caught up with Edgar Uaje, senior product manager at Experian, to find out more about APIs in the financial services space. What exactly are APIs and why are they so important? And how do they apply to B2B? APIs are the building blocks of many of our applications that exist today. They are an intermediary that allows application programs to communicate, interact, and share data with various operating systems or other control programs. In B2B, APIs allow our clients to consume our data, products, and services in a standard format. They can utilize the APIs for internal systems to feed their risk models or external applications for their customers. As Experian has new data and services available, our clients can quickly access the data and services. Are APIs secure? APIs are secure as long as the right security measures are put in place. There are many security measures that can be utilized such as authentication, authorization, channel encryption and payload encryption. Experian takes security seriously and ensures that the right security measures are put in place to protect our data. For example, one of the recent APIs that was built this year utilizes OAuth, channel encryption, and payload encryption. The central role of APIs is promoting innovation and rapid but stable evolution, but they seem to only have taken hold selectively in much of the business world. Is the world of financial services truly ready for APIs? APIs have been around for a long time, but they are getting much more traction recently. Financial tech and online market place lending companies are leading the charge of consuming data, products, and services through APIs because they are nimble and fast. With standard API interfaces, these companies can move as fast as their development teams can. The world of financial services is evolving, and the time is now for them to embrace APIs in day-to-day business. How can APIs benefit a bank or credit union, for example? APIs can benefit a bank or credit union by allowing them to consume Experian data, products, and services in a standard format. The value to them is faster speed to market for applications (internal/external), ease of integration, and control over the user’s experience. APIs allow a bank or credit union to quickly develop new and innovative applications quickly, with the support of their development teams. Can you tell us more about the API Developer Portal? Experian will publish the documentation of our available APIs on our Developer Portal over time as they become available. Our clients will have a one-stop shop to view available APIs, review API documentation, obtain credentials, and test APIs. This is simplifying data access by utilizing REST API, making it easier for our clients.

Since the advent of the internet, our lives have changed drastically for the better. We can perform many of life’s daily activities from the comfort of our own home. According to Aite, in 2016 alone 36 million Americans made some form of mobile payment — paying a bill, purchasing something online, paying for fast food or making a mobile wallet purchase at a retailer. Simply put, the internet has made our lives easier. But with the good also comes the bad. While most consumers have moved to the digital world, so have fraudsters. With minimal risk and high reward at stake, e-commerce fraud attacks have increased dramatically over the last few years, with no signs of slowing down. We recently analyzed millions of transactions from the first half of 2017 to identify fraud attack rates based on billing and shipping addresses and broke down the findings into various geographic trends. Fraud attack rates represent the attempted fraudulent e-commerce transactions against the population of overall e-commerce orders. Consumers living out West and in the South have experienced more than their fair share of fraud. During the first half of 2017, the West and the South were the top two regions for both billing and shipping attacks. While both regions were at the top during the same time last year, the attacks themselves have increased substantially. Given the proximity to seaports and major international airports, this is somewhat unsurprising — particularly for shipping fraud — as many fraudsters will leverage reshippers to transport goods soon after delivery. .dataTb{margin:20px auto;width:100%}.dataTb:after{clear:both}.dataTb table{}.dataTb td,.dataTb th{border:1px solid #ddd;padding:.8em}.dataTb th{background:#F4F4F4}.tbL{float:left;width:49%}.tbR{float:right;width:49%;margin:0 0 0 2%} Shipping: Riskiest Regions Region Attack rate West 38.1 South 32.1 Northeast 27.0 North Central 20.7 Billing: Riskiest Regions Region Attack rate West 37.2 South 32.9 Northeast 27.3 North Central 24.0 At the state level, the top three shipping fraud states remained the same as 2016 — Delaware, Oregon and Florida — but the order changed. Oregon was the most targeted, with a fraud rate of 135.2 basis points, more than triple its rate at in the end of 2016. Though no longer in the top spot, Delaware saw alarming spikes as well, with shipping attack rates nearly triple last year’s rate at 128.6 basis points and billing attacks at 79.6 basis points. .dataTb{margin:20px auto;width:100%}.dataTb:after{clear:both}.dataTb table{}.dataTb td,.dataTb th{border:1px solid #ddd;padding:.8em}.dataTb th{background:#F4F4F4}.tbL{float:left;width:49%}.tbR{float:right;width:49%;margin:0 0 0 2%} Shipping: Riskiest States State Attack rate Oregon 135.2 Delaware 128.2 Florida 57.4 New York 45.0 Nevada 36.9 California 36.9 Georgia 33.5 Washington, D.C 30.8 Texas 29.6 Illinois 29.4 Billing: Riskiest States Region Attack rate Oregon 87.5 Delaware 79.6 Washington, D.C. 63.0 Florida 47.4 Nevada 38.8 California 36.9 Arkansas 36.6 New York 35.5 Vermont 34.2 Georgia 33.4 Diving a bit deeper, ZIPTM codes in Miami, Fla., make up a significant portion of the top 10 ZIP CodeTM lists for shipping and billing attacks — in fact, many of the same ZIP codes appear on both lists. The other ZIP Code that appears on both lists is South El Monte, Calif., which has a high percentage of industrial properties — common targets for fraudsters to ship packages, then reship overseas. You can download the top 100 riskiest Zip Codes in the U.S. for H1 2017. .dataTb{margin:20px auto;width:100%}.dataTb:after{clear:both}.dataTb table{}.dataTb td,.dataTb th{border:1px solid #ddd;padding:.8em}.dataTb th{background:#F4F4F4}.tbL{float:left;width:49%}.tbR{float:right;width:49%;margin:0 0 0 2%} Shipping: Top 10 riskiest ZIP™ Codes ZIP Code Attack rate 33122 [Miami, Fla.] 2409.4 91733 [South El Monte, Calif.] 1655.5 33198 [Miami, Fla.] 1295.2 33166 [Miami, Fla.] 1266.0 33195 [Miami, Fla.] 1037.3 33192 [Miami, Fla.] 893.9 97251 [Portland, Ore.] 890.6 07064 [Port Reading, NJ] 808.9 89423 [Minden, Nev.] 685.5 77072 [Houston, Tex.] 629.3 Billing: Top 10 riskiest ZIP™ Codes ZIP Code Attack rate 77060 [Houston, Tex.] 1337.6 33198 [Miami, Fla.] 1215.6 33122 [Miami, Fla.] 1106.2 33166 [Miami, Fla.] 1037.4 91733 [South El Monte, Calif.] 780.1 33195 [Miami, Fla.] 713.7 97252 [Portland, Ore.] 670.8 33191 [Miami, Fla.] 598.8 33708 [St. Petersburg, Fla.] 563.6 33792 [Miami, Fla.] 493.0 As e-commerce fraud continues to grow, businesses need to be proactive to keep themselves and their customers safe. That means incorporating multiple, layered fraud prevention strategies that work together seamlessly — for example, understanding details about users and their devices, knowing how users interact with the business and evaluating previous transaction history. This level of insight can help businesses distinguish real customers from nefarious ones without impacting the customer experience. While businesses are ultimately responsible for the safety of customers and their data, the onus doesn’t rest solely with them. Consumers should also be vigilant when it comes to protecting their digital identities and payment information. That means creating strong, unique passwords; actively monitoring online accounts; and using two-factor authentication to secure account access. At the end of the day, e-commerce fraud is a challenge that businesses and consumers will experience for the foreseeable future. But rising attack rates don’t have to spell doom and gloom for the industry. E-commerce growth is still extremely strong, as consumers interact through multiple channels (in-store, mobile and web) and expect a personalized experience. Establishing trust and verifying digital identities are key to meeting these latest expectations, which provide new opportunities for businesses and consumers to interact seamlessly and transact securely. With multiple safeguards in place, businesses have a variety of options to protect their customers and their brand reputation. Experian is a nonexclusive full-service provider licensee of the United States Postal Service®. The following trademarks are owned by the United States Postal Service®: ZIP and ZIP Code. The price for Experian’s services is not established, controlled or approved by the United States Postal Service.

We regularly hear from clients that charge-offs are increasing and they’re struggling to keep up with the credit loss. Many clients use the same debt collection strategy they’ve used for years – when businesses or consumers can’t repay a loan, the creditor or collection agency aggressively contacts them via phone or mail to obtain repayment – never considering the customer experience for the debtor. Our data shows that consumers accounted for $37.24 billion in bankcard charge-offs in Q2 2017, a 17.1 percent increase from Q2 2016. Absorbing credit losses at such a high rate can impact the sustainability of the institution. Clearly the process could use some adjusting. Traditionally, debt collection has been solely about the money. The priority was ensuring that as much of the outstanding debt as possible was repaid. But collecting needs to be about more than that. It also should focus on the customer and his or her individual situation. When it comes to debt collection, customers should not all be treated the same way. I recently shared some tips in Credit Union Business Magazine about how to actively engage and collect from members. The same holds true for other financial institutions – they need to know the difference between a customer who has simply forgotten to make a payment and one who is dealing with financial hardship. As an example, if a person is current on his or her mortgage payment but has slipped behind on his or her credit card payment, that doesn’t necessarily signify financial hardship. It’s an opportunity to work with the customer to manage the debt and get back to current. Modern financial institutions build acquisition and customer management strategies targeted at individuals, so why should the collection process be any different? The challenge is keeping the customer at the center while also managing against potential increases in delinquencies. This holistic approach may be slightly more complex, but technology and analytics will simplify the process and bring about a more engaging experience for customers. The Power of Data and Technology Instead of relying on the same outdated collections approach – which results in uncomfortable exchanges on the phone that don’t ensure repayment –leverage data to your advantage. The data and technology exists to help you make more informed decisions, such as: What’s the most effective communication channel to reach the defaulting customer? When should you contact him or her? How often? The best course of action could be high-touch outreach, but sometimes doing nothing is the right approach. It all depends on the situation. Data and analytics can help uncover which customers are most likely to pay on their own and those who may need a little more help, allowing you to adjust your treatment strategy accordingly. By catering to the preferences of the customer, there’s a greater chance for a positive experience on both sides. The results: less charge-off debt, higher customer satisfaction and a stronger relationship. Explore the Digital Age In 2016, 36 million Americans made some form of mobile payment—paying a bill, purchasing something online, or paying for fast food, or making a Mobile Wallet purchase at a retailer. By 2020, nearly 184 million consumers will have done so, according to Aite. Consumers expect and deserve convenience. In the digital world, financial institutions have an opportunity to provide that expectation and then some. Imagine a customer being able to negotiate and manage his or her past-due account virtually, in the privacy of his or her own home, when it’s most convenient, to set their payment dates and terms. Luckily, the technology exists to make this vision a reality. Customers, not money, need to be at the heart of every debt collections strategy. Gone are the days of mass phone calls to debtors. That strategy made consumers unhappy, embarrassed and resentful. Successful debt collection comes down to a basic philosophy: Treat customers and his or her unique situation individually rather than as a portfolio profile. The creditors who live by that philosophy have an opportunity to reap the rewards on the back-end.

School is nearly back in session. You know what that means? The next wave of college students is taking out their first student loans. It’s a milestone moment – and likely the first trade on the credit file for many of these individuals. According to the College Board, the average cost of tuition and fees for the 2016–2017 school year was $33,480 at private colleges, $9,650 for state residents at public colleges, and $24,930 for out-of-state residents attending public universities. So really, regardless of where students go, the cost of a college education is big. In fact, from January 2006 to July 2016, the Consumer Price Index for college tuition and fees increased 63 percent. So, unless mom and dad did a brilliant job saving, chances are many of today’s students will take on at least some debt to foot the college bill. But it’s not just the young who are consumed by student loan debt. In Experian’s latest State of Student Lending report, we dive into how the $1.4 trillion in student loan debt for Americans is impacting all generations in regards to credit scores, debt load and delinquencies. The document additionally looks at geographical trends, noting which states have the most consumers with student loan debt and which ones have the least. Overall, we discovered 13.4% of U.S. consumers have one or more student loan balances on their credit file with an average total balance of $34k. Additionally, these consumers have an average of 3.7 student loans with 1.2 student loans in deferment. The average VantageScore® credit score for student loan carriers is 650. As we looked across the generations, every group – from the Silents (age 70+) to Gen Z (oldest are between 18 to 20) had some student loan debt. While we can make assumptions that the Silents and Boomers are likely taking out these loans to support the educational pursuits of their children and grandchildren, it can be mixed for Gen X, who might still be paying off their own loans and/or supporting their own kids. Gen X members also reported the largest average student loan total balance at $39,802. Gen Z, the newest members to the credit file, have just started to attend college, thus their generation has the largest percent of student loan balances in deferment at 77%. Their average student loan total balance is also the lowest of all generations at $11,830, but that is to be expected given their young ages. In regards to geographical trends, the Northern states tended to sport the highest average student loan total balances, with consumers in Washington D.C. winning that race with $52.5k. Southern states, on the other hand, reported higher percentages of consumers with student loan balances 90+ days past due. South Carolina, Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas and Texas held the top spots in the delinquency category. Access the complete State of Student Lending report. Data from this report is representative of student loan data on file as of June 2017.

We live in a digital world where online identities are ubiquitous. But with the internet’s inherent anonymity, how do you know you’re interacting with a legitimate individual rather than an imposter? Too often we hear stories about consumers who see unauthorized purchases on their credit cards, enable access to their devices based on an imposter claiming to be a security vendor or send money to someone they met online only to learn they’ve been “catfished” by a fraudster. These are growing problems, as more consumers transition to digital services and look to businesses to protect them, enable seamless trusted interactions and maintain their privacy. I recently chatted with MarketWatch about how consumers can protect themselves and their privacy when using online dating apps, as well as what businesses are doing to safeguard digital data. As part of the discussion, I mentioned that a simple, standard verification process companies of all sizes can leverage is vital to our rapidly evolving digital economy. Today, companies have their own policies, processes and definitions of identity verification, depending on the services they offer. This ranges from secure access requiring strong identity proofing, document verification, multifactor authentication and biometric enrollment to new social profiles that do little more than validate receipt of an email to establish an online account. To satisfy those diverse risk-based needs, more organizations are turning to federated identity verification options. A federated system allows businesses to leverage trusted, reputable, third-party sources to validate identity by cross-referencing the information they’ve received from a consumer against these sources to determine whether to establish an account or allow a transaction. While some organizations have attempted to develop similar identity verification capabilities, many lack a trusted identity source. For example, there are solutions that leverage data from social media accounts or provide multifactor fraud and authentication options, but they often become easily compromised because of the absence of verifiable data. A trusted solution aggregates data across multiple providers that have undergone thorough security and data quality vetting to ensure the identity data is accurately submitted in accordance with business and compliance requirements. In fact, there are only a handful of trusted identity sources with this level of due diligence and oversight. At Experian, we assess verification requests against an aggregate of hundreds of millions of records that include identity relationships, profile risk attributes, historical usage records and demographic data assets. With decades of knowledge about identity management and fraud prevention, we help companies of all sizes balance risk mitigation and maintain compliance requirements — all while ensuring consumer data privacy. Trust takes years to build and mere seconds to lose, and the industry has made undeniable progress in security. But there is much left to do. Consumers are increasingly involved in the protection and use of their data. However, they often don’t realize downloading a hot new app and entering personal details or linking to their friends exposes them to unnecessary risk. It’s important for businesses to be clear about their identity verification processes so consumers can make educated decisions before electing to provide invaluable identity data. The most effective fraud prevention and identity strategy is one that quickly establishes trust without inconveniencing the consumer. By staying up to date on verification methods, businesses can ensure customers have a smooth, personalized and engaging online experience.

Many institutions take a “leap of faith” when it comes to developing prospecting strategies as it pertains to credit marketing. But effective strategies are developed from deep, analytical analysis with clearly identified objectives. They are constantly evolving – no setting and forgetting. So what are the basics to optimizing your prospecting efforts? Establish goals Unfortunately, far too many discussions begin with establishing targeting criteria before program goals are set. But this leads to confusion. Developing targeting criteria is kind of like squeezing a balloon; when you restrict one end, the other tends to expand. Imagine the effect of maximizing response rates when soliciting new loans. If no other criteria are considered, you could end up targeting high-risk individuals who cannot get approved elsewhere. Obviously, we’re not interested in increasing originations at all cost; risk must be understood as well. But this is where things get complicated. Lower-risk consumers tend to be the most coveted, get the best offers, and therefore have lower response rates and margins. Simplicity is best The US Navy developed the KISS acronym (keep it simple, stupid) in the 1960s on the philosophy that complexity increases the probability of error. This is largely true in targeting methodologies, but don’t mistake limiting complexity for simplicity. Perhaps the most simplistic approach to prescreen credit marketing is using only risk criteria to set an eligible population. Breaking a problem down to this single dimension generally results in low response rates and wasted budget. Propensity models and estimated interest rates are great tools for identifying consumers that are more likely to respond. Adding them as an additional filter to a credit-qualified population can help increase response rates. But what about ability to pay? So far we’ve considered propensity to open and risk (the latter being based on current financial obligations). Imagine a consumer with on-time payment behavior and a solid credit score who takes a loan only to be unable to meet their obligations. You certainly don’t want to extend debt that will cause a consumer to be overextended. Instead of going through costly income verification, income estimation models can assist with identifying the ability to repay the loan you are marketing. Simplicity is great, but not to the point of being one-dimensional. Take off the blindfold Even in the days of smartphones and GPS navigation, most people develop a plan before setting off on a road trip. In the case of credit marketing, this means running an account review or archive analysis. Remember that last prescreen campaign you ran? What could have happened with a more sophisticated targeting strategy? Having archive data appended to a past marketing campaign allows for “what if” retrospective analysis. What could response rates have been with a propensity tool? Could declines due to insufficient income have been reduced with estimated income? Archive data gives 20/20 hindsight to what could have been. Just like consulting a map to determine the shortest distance to a destination or the most scenic route, retrospective analysis on past campaigns allows for proactive planning for future efforts. Practice makes perfect Even with a plan, you probably still want to have the GPS running. Traffic could block your planned route or an unforeseen detour could divert you to a new path. Targeting strategies must continually be refined and monitored for changes in customer behavior. Test and control groups are essential to continued improvement of your targeting strategies. Every campaign should be analyzed against the goals and KPIs established at the start of the process. New hypotheses can be evaluated through test populations or small groups designed to identify new opportunities. Let’s say you typically target consumers in a risk range of 650-720, but an analyst spots an opportunity where consumers with a range of 625-649 with no delinquencies in the past 12 months performs nearly at the rate of the current population. A small test group could be included in the next campaign and studied to see if it should be expanded in future campaigns. Never “place bets” Assumptions are only valid when they are put to the test. Never dive into a strategy without testing your hypothesis. The final step in implementing a targeting strategy should be the easiest. If goals are clearly understood and prioritized, past campaigns are analyzed, and hypotheses are laid out with test and control groups, the targeting criteria should be obvious to everyone. Unfortunately, the conversation usually starts at this phase, which is akin to placing bets at the track. Ever notice that score breaks are discussed in round numbers? Consider the example of the 650-720 range. Why 650 and not 649 or 651? Without a test and learn methodology, targeting criteria ends up based on conventional wisdom – or worse, a guess. As you approach strategic planning season, make sure you run down these steps (in this order) to ensure success next year. Establish program goals and KPIs Balance simplicity with effectiveness Have a plan before you start Begin with an archive Learn and optimize In God we trust, all others bring data

Historical data that illustrates lower credit card use and increases in payments is key to finding consumers whose credit trajectory is improving. But positive changes in consumer behavior—especially if it happens slowly over time—don’t necessarily impact a consumer’s credit score. And many lenders are missing out on capturing new business by failing to take a closer look. It’s easy to categorize consumers by their credit score alone, but you owe it to your bottom line to investigate further: Are the consumer’s overall payments increasing? Is his credit card utilization decreasing? Are the overall card balances remaining consistent or declining? Could the consumer be within your credit score guidelines within a month or two? And most importantly, could a competitor acquire the consumer a month or two after you declined him? Identifying new customers who previously used credit responsibly is relatively easy since they typically have rich credit profiles that may include a mortgage and numerous types of credit accounts. But how do you evaluate consumers who may look identical? Trended data and attributes provide insight into whether a consumer is headed in the right direction: With more than 613 trended attributes available for real-time decisioning and for batch campaigns, Experian trends key factors that provide the insight needed for lenders to lend deeper without sacrificing credit quality. Looking at trended data and attributes is critical for portfolio growth, and credit line increases based on good credit behavior is a must for lenders for two reasons. First, you’ve already spent the money acquiring the consumer and you should not waste the opportunity to maximize returns. Second, competition is fierce; another lender could reward the consumer for great credit behavior they’ve displayed with your company. Be there first, be consistent, or be left behind. Use Experian’s Payment Stress Attributes and Short-term Utilization Attributes in custom scores or swap-set strategies in order to find quality customers who may be worthy of line increases or other attribute credit terms. Look to trended data to swap in consumers who may fall within a few points under your credit score guidelines, and reward your existing customers before another lender does. Near-prime consumers of today are the prime consumers of tomorrow.

1 in 10 Americans are living paycheck to paycheck Financial health means more than just having a great credit score or money in a savings account. It includes being able to manage daily finances, save for the future and weather a financial shock. Here are some facts about Americans’ financial health: 46% of Americans are struggling financially. Roughly 31% of nonretired adults have no retirement savings or pension. Approximately 50% are unprepared for a financial emergency, and about 1 in 5 have no savings set aside to cover unexpected emergencies. It’s never too late for people to achieve financial health. By providing education on money management, you can drive new opportunities for increased engagement, loyalty and long-term revenue streams. Why financial health matters >

School’s out, and graduation brings excitement, anticipation and bills. Oh, boy, here come the student loans. Are graduates ready for the bills? Even before they have a job lined up? With lots of attention from the media, I was interested in analyzing student loan debt to see if this is a true issue or just a headline grab. There’s no shortage of headlines alluding to a student loan crisis: “How student loans are crushing millennial entrepreneurialism” “Student loan debt in 2017: A $1.3 trillion crisis” “Why the student loan crisis is even worse than people think” Certainly sounds like a crisis. However, I’m a data guy, so let’s look at the data. Pulling from our data, I analyzed student loan trades for the last four years starting with outstanding debt — which grew 21 percent since 2013 to reach a high of $1.49 trillion in the fourth quarter of 2016. I then drilled down and looked at just student loan trades. Created with Highstock 5.0.7Total Number of Student Loans TradesStudent Loan Total TradesNumber of trades in millions174,961,380174,961,380182,125,450182,125,450184,229,650184,229,650181,228,130181,228,130Q4 2013Q4 2014Q4 2015Q4 2016025M50M75M100M125M150M175M200MSource: Experian (function(){ function include(script, next) {var sc=document.createElement("script");sc.src = script;sc.type="text/javascript";sc.onload=function() {if (++next < incl.length) include(incl[next], next);};document.head.appendChild(sc);}function each(a, fn){if (typeof a.forEach !== "undefined"){a.forEach(fn);}else{for (var i = 0; i < a.length; i++){if (fn) {fn(a[i]);}}}}var inc = {},incl=[]; each(document.querySelectorAll("script"), function(t) {inc[t.src.substr(0, t.src.indexOf("?"))] = 1;});each(Object.keys({"https://code.highcharts.com/stock/highstock.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/adapters/standalone-framework.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-more.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-3d.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/data.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/exporting.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/funnel.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/solid-gauge.js":1}),function (k){if (!inc[k]) {incl.push(k)}});if (incl.length > 0) { include(incl[0], 0); } function cl() {if(typeof window["Highcharts"] !== "undefined"){new Highcharts.Chart("highcharts-79eb8e0a-4aa9-404c-bc5f-7da876c38b0f", {"chart":{"type":"column","inverted":true,"polar":false,"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"plotOptions":{"series":{"dataLabels":{"enabled":true},"animation":true}},"title":{"text":"Student Loan Total Trades","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"bold","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#333333","width":"792px"}},"subtitle":{"text":"","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#666666","width":"792px"}},"exporting":{},"yAxis":[{"title":{"text":"Number of trades in millions","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"labels":{"format":""},"type":"linear"}],"xAxis":[{"title":{"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"},"text":""},"reversed":true,"labels":{"format":"{value:}"},"type":"linear"}],"series":[{"data":[["Total Student Loans",174961380]],"name":"Q4 2013","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":0,"_symbolIndex":0},{"data":[["Total Student Loans",182125450]],"name":"Q4 2014","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":1,"_symbolIndex":1},{"data":[["Total Student Loans",184229650]],"name":"Q4 2015","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":2,"_symbolIndex":2},{"data":[["Total Student Loans",181228130]],"name":"Q4 2016","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":3,"_symbolIndex":3}],"colors":["#26478d","#406eb3","#632678","#982881"],"legend":{"itemStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal","cursor":"pointer"},"itemHiddenStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#cccccc","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"},"layout":"horizontal","floating":false,"verticalAlign":"bottom","x":0,"align":"center","y":0},"credits":{"text":"Source: Experian"}});}else window.setTimeout(cl, 20);}cl();})(); Over the past four years, student loan trades grew 4 percent, but saw a slight decline between 2015 and 2016. The number of trades isn’t growing as fast as the amount of money that people need. The average balance per trade grew 17 percent to $8,210. Either people are not saving enough for college or the price of school is outpacing the amount people are saving. I shifted the data and looked at the individual consumer rather than the trade level. Created with Highstock 5.0.7Student Loan Average Balance per Trade4.044.043.933.933.893.893.853.85Q4 2013Q4 2014Q4 2015Q4 201600.511.522.533.544.5Source: Experian (function(){ function include(script, next) {var sc=document.createElement("script");sc.src = script;sc.type="text/javascript";sc.onload=function() {if (++next < incl.length) include(incl[next], next);};document.head.appendChild(sc);}function each(a, fn){if (typeof a.forEach !== "undefined"){a.forEach(fn);}else{for (var i = 0; i < a.length; i++){if (fn) {fn(a[i]);}}}}var inc = {},incl=[]; each(document.querySelectorAll("script"), function(t) {inc[t.src.substr(0, t.src.indexOf("?"))] = 1;});each(Object.keys({"https://code.highcharts.com/stock/highstock.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/adapters/standalone-framework.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-more.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-3d.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/data.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/exporting.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/funnel.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/solid-gauge.js":1}),function (k){if (!inc[k]) {incl.push(k)}});if (incl.length > 0) { include(incl[0], 0); } function cl() {if(typeof window["Highcharts"] !== "undefined"){new Highcharts.Chart("highcharts-66c10c16-1925-40d2-918f-51214e2150cf", {"chart":{"type":"column","polar":false,"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"},"inverted":true},"plotOptions":{"series":{"dataLabels":{"enabled":true},"animation":true}},"title":{"text":"Student Loan Average Number of Trades per Consumer","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"bold","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#333333","width":"356px"}},"subtitle":{"text":"","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#666666","width":"356px"}},"exporting":{},"yAxis":[{"title":{"text":"","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"14px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"type":"linear","labels":{"format":"{value}"}}],"xAxis":[{"title":{"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"14px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"type":"linear","labels":{"format":"{}"}}],"colors":["#26478d","#406eb3","#632678","#982881","#ba2f7d"],"series":[{"data":[["Average Trades per Consumer",4.04]],"name":"Q4 2013","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":0},{"data":[["Average Trade per Consumer",3.93]],"name":"Q4 2014","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":1},{"data":[["Average Trade per Consumer",3.89]],"name":"Q4 2015","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":2},{"data":[["Average Trades per Consumer",3.85]],"name":"Q4 2016","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":3}],"legend":{"floating":false,"itemStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"bold","fontStyle":"normal","cursor":"pointer"},"itemHiddenStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#cccccc","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"},"layout":"horizontal"},"credits":{"text":"Source: Experian"}});}else window.setTimeout(cl, 20);}cl();})(); The number of overall student loan trades per consumer is down to 3.85, a decrease of 5 percent over the last four years. This is explained by an increase in loan consolidations as well as the better planning by students so that they don’t have to take more student loans in the same year. Lastly, I looked at the average balance per consumer. This is the amount that consumers, on average, owe for their student loan trades. Created with Highstock 5.0.7Balance in thousands ($)Quarterly $USD Debt per ConsumerQ4 Student Loan TrendsAverage Student Loan Debt Balance per Consumer27,93427,93429,22629,22630,52330,52332,06132,061Q4 2013Q4 2014Q4 2015Q4 201605,00010,00015,00020,00025,00030,00035,000Source: Experian (function(){ function include(script, next) {var sc=document.createElement("script");sc.src = script;sc.type="text/javascript";sc.onload=function() {if (++next < incl.length) include(incl[next], next);};document.head.appendChild(sc);}function each(a, fn){if (typeof a.forEach !== "undefined"){a.forEach(fn);}else{for (var i = 0; i < a.length; i++){if (fn) {fn(a[i]);}}}}var inc = {},incl=[]; each(document.querySelectorAll("script"), function(t) {inc[t.src.substr(0, t.src.indexOf("?"))] = 1;});each(Object.keys({"https://code.highcharts.com/stock/highstock.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/adapters/standalone-framework.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-more.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/highcharts-3d.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/data.js":1,"https://code.highcharts.com/modules/exporting.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/funnel.js":1,"http://code.highcharts.com/modules/solid-gauge.js":1}),function (k){if (!inc[k]) {incl.push(k)}});if (incl.length > 0) { include(incl[0], 0); } function cl() {if(typeof window["Highcharts"] !== "undefined"){Highcharts.setOptions({lang:{"thousandsSep":","}});new Highcharts.Chart("highcharts-0b893a55-8019-4f1a-9ae1-70962e668355", {"chart":{"type":"column","inverted":true,"polar":false,"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"plotOptions":{"series":{"dataLabels":{"enabled":true},"animation":true}},"title":{"text":"Average Student Loan Balance per Consumer","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"bold","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#333333","width":"308px"}},"subtitle":{"text":"","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal","fill":"#666666","width":"792px"}},"exporting":{},"yAxis":[{"title":{"text":"Balance numbers are in thousands ($)","style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"labels":{"format":"{value:,1f}"},"reversed":false}],"xAxis":[{"title":{"style":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#666666","fontSize":"16px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"},"text":"Balance in thousands ($)"},"labels":{"format":"{value:}"},"type":"linear","reversed":true,"opposite":false}],"series":[{"data":[["Average Balance per Consumer",27934]],"name":"Q4 2013","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":0},{"data":[["Average Balance per Consumer",29226]],"name":"Q4 2014","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":1},{"data":[["Average Balance per Consumer",30523]],"name":"Q4 2015","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":2},{"data":[["Average Balance per Consumer",32061]],"name":"Q4 2016","turboThreshold":0,"_colorIndex":3}],"colors":["#26478d","#406eb3","#632678","#982881"],"legend":{"itemStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#333333","fontSize":"12px","fontWeight":"bold","fontStyle":"normal","cursor":"pointer"},"itemHiddenStyle":{"fontFamily":"Arial","color":"#cccccc","fontSize":"18px","fontWeight":"normal","fontStyle":"normal"}},"lang":{"thousandsSep":","},"credits":{"text":"Source: Experian"}});}else window.setTimeout(cl, 20);}cl();})(); Here we see a growth of 15 percent over the last four years. At the end of 2016, the average person with a student loan balance had just over $32,000 outstanding. While this is a large increase, we should compare it with other purchases: This balance is no more than a person purchasing a brand-new car without a down payment. While we’re seeing an increase in overall outstanding debt and individual loan balances, I’m not yet agreeing that this is the crisis the media portrays. If students are educated about the debt that they’re taking out and making sure that they’re able to repay it, the student loan market is performing as it should. It’s our job to help educate students and their families about making good financial decisions. These discussions need to be had before debt is taken out, so it’s not a shock to the student upon graduation.

There’s a new crew coming of age. Enter Generation Z. Gen Z — those born between the mid-1990s and the early 2000s — makes up one-quarter of the U.S. population. By 2020, they’ll account for 40% of all consumers. The oldest members of this next cohort — 18- to 20-year-olds — are coming of age. Here are some insights on how this initial segment of Gen Z is beginning to use credit. Credit scores averaged 631 in 2016. Debt levels — consisting largely of bankcards and auto and student loans — are low, with an average debt-to-income ratio of just 5.7%. Average income is $33,800. This generation is being raised in an era of instant, always-on access. They expect a quick, seamless and customized mobile experience. You have just 8 seconds to capture their attention. Webinar: A First Look at Gen Z and Credit