Industries

Leveraging customer intelligence in the age of mass data compromise Hardly a week goes by without the media reporting a large-scale hack of sensitive personal or account information. Increasingly, the public seems resigned to believe that such compromises are the new normal, producing a kind of breach fatigue that may be lowering the expectations consumers have for identity and online security. Still, businesses must be vigilant and continue to apply comprehensive, data-driven intelligence that helps to thwart both breaches and the malicious use of breached information and to protect all parties’ interests. We recently released a new white paper, Data confidence realized: Leveraging customer intelligence in the age of mass data compromise, to help businesses understand how data and technology are needed to strengthen fraud risk strategies through comprehensive customer intelligence. At its core, reliable customer intelligence is based on high-quality contextual identity and device attributes and other authentication performance data. Customer intelligence provides a holistic, bound-together view of devices and identities that equips companies and agencies with the tools to balance cost and risk without increasing transactional friction and affecting the customer experience. In the age of mass data compromise, however, obtaining dependable information continues to challenge many companies, usually because consumer-provided identities aren’t always unique enough to produce fully confident decisioning. For more information, and to get a better sense of what steps you need to take now, download the full white paper.

Environmentally friendly, lower fuel costs and tax incentives. These are all words that describe alternative-powered vehicles, and serve as reasons why many car shoppers flocked to their local dealerships over the past several years with the intent of “going green” with their next vehicle. However, that trend seems to be fading into the past. As gas prices continue to trend downward, we have seen more and more consumers steer away from hybrids. In fact, according to Experian’s recent Automotive Market Trends and Registrations analysis, when it came to fuel type, hybrids only made up 2.5 percent of the vehicles registered in the third quarter of 2015. This was a 19.2 percent drop from a year ago. Meanwhile, gas-powered vehicles dominated the market at nearly 94 percent. Furthermore, the analysis found that the hybrid car was the vehicle segment that suffered the second largest year-over-year decrease in registrations and its second consecutive quarterly decline, reducing by 19 percent. Conversely, the upper premium sports car (including vehicle models, such as the Porsche 911, Jaguar XJ and BMW 6-Series) saw the highest percentage increase, growing by 45 percent over the same time period. From an overall market perspective, the analysis found that through the third quarter of 2015, new vehicle registrations increased by 5.5 percent from the previous year – a clear sign that the market continues to trend in a positive direction. As previous Experian analyses have indicated, as long as consumers continue to stay on top of their monthly payments, the boom in new vehicle sales will be a positive sign for the industry. The analysis also examined the demographic characteristics of the new vehicle buyer, and found that nearly 50 percent of the new vehicle purchasing power in the U.S. falls to consumers between the ages of 40-69. What’s more, individuals with incomes from $50,000-$100,000 made up 35.5 percent of all new vehicle buyers. Like many things in life, the automotive market is ever changing. At one moment, a segment of vehicles could be selling like hot cakes, and the next moment suffer a steep decline in sales. Gaining insight into these types of trends enables manufacturers and retailers to better understand the fluctuations in the market, and more easily position their businesses for success. And the better positioned they are for success, the more “green” these companies will see.

Experian data shows consumers are more confident managing their credit since the recession. The Q3 2015 Experian Market Intelligence Brief was released today featuring data that highlights consumer credit card debt has now reached its highest level since Q4 2009. Credit card debt levels reached $650 billion in Q3 2015, the highest it has been since Q4 2009 when it was $667 billion. Credit card delinquency rates on outstanding balances 60 or more days past due have decreased 71 percent during the same time period. Combining those indicators with the national unemployment rate dropping 50 percent during the same span illustrates a positive economic outlook on credit card trends among lenders and consumers. “Overall credit card limits have increased 102 percent since Q4 2009 with $82 billion originated in Q3 2015,” said Kelly Kent, vice president of Experian Decision Analytics. “The increase in limits from lenders and the steady climb in credit card debt combined with exceptional delinquency rates signals greater confidence among consumers as they are showing more assurance in managing their credit since the recession. We expect to see credit card debt increase in Q4 based on historical seasonal trends driven by the holiday shopping season especially with the early positive holiday sales as a sign.” The Q3 2015 Experian Market Intelligence Brief report is now available.

Last December, American Banker named online marketplace lending its innovation of the year as a result of the “industry’s rapid growth and evolution.” Meanwhile, in 2015, millennials scored headlines in nearly every publication imaginable – industries, politicians and academics all trying to understand and articulate how the now largest-living generation will influence how we work, live and lead. So perhaps it’s no surprise the two hot topics have collided this year. Gen Y is tech-dependent and Internet-enabled. They have increasingly grown to expect the tools and services they use to be available online, including anything and everything in the financial services space. Marketplace lenders are ever-so eager to sweep in and serve. Online and mobile solutions are certainly one thing, but Experian’s latest research reveals this generation is also very receptive to “non-bank” lenders for the ease, speed and accessibility they provide. 47 percent of millennials said they are likely to use alternative finance sources in the near future 57 percent reported they are willing to use alternative companies and services that innovate to meet their needs 13 percent said they’ve already taken out a loan from an alternate or non-bank lender As they come of age, hitting those big milestones – college graduations, marriage, starting families, making home purchases – Gen Y is wading through its financial options. Research and logic suggest millennials will without a doubt have a greater openness toward nontraditional banking, representing a huge market for online marketplace lenders. For the millennial entrepreneurs especially, marketplace lending is proving to be a good fit. “They are on the earlier curve of their small business ownership and entrepreneurial paths,” David Solis, sales performance manager at Bank of America, told CNN Money. “It makes sense they’re going to be pursuing alternative forms of lending.” Affluent millennials are another segment open to alternative financial services. A 2015 LinkedIn study on this specific target stated affluent millennials are particularly likely to envision a cashless, sharing-based economy in the future, where banks no longer serve as their primary financial institutions. Nearly seven out of 10 affluent millennials are likely to consider such offerings outside of the traditional financial services space, compared to just 47 percent of affluent Gen X’ers. The millennial generation may not fully understand all products traditional banks offer, since they rarely set foot in “brick-and-mortar” establishments, but they are a prime market for online investing and lending services. They’re more experimental, more digital, less loyal. In short, they are looking for financial services that are as tech-savvy as they are; those who don’t keep up may get left behind, and online marketplace lenders are certainly positioning themselves to win over this generation. To be most successful in capturing this highly sought-after generation, online marketplace lenders will need to continue to innovate both in terms of differentiating their product offerings and getting more sophisticated in their targeted marketing approach. As the online marketplace continues to expand with more players, heating up with increased competition, segmentation strategies will be key in finding the right borrowers and matching them with the right offer. As we head into 2016, there is no doubt many will continue to monitor the financial services trends emerging. Chances are online marketplace lenders and millennials will likely be attached to many of the headlines. For more information, visit www.experian.com/marketplacelending.

The financial services industry continues to face mounting pressures to meet the highest standards of data reporting and accuracy. New regulations and mandates are introduced regularly, impacting the way companies do business. And a more credit-educated consumer base is seeking insights into their own credit data, providing a separate second of eyes that demand accuracy. Not only has the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) set requirements on dispute investigation and response, but the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) is also paying close attention. Recent announcements indicate the CFPB wants more information about the credit eco-system to gain more data about consumer disputes. According to the CFPB, it’s a joint problem – “the NCRAA’s, data furnishers, public record providers, and consumers all play roles which affect the accuracy of the information with credit reports.” And it’s not just the big banks that are being targeted with fines. The CFPB has made it clear it will also direct attention to certain nonbanks and financial products. In today’s data-driven environment, there are roughly 12,000-plus data furnishers, resulting in more than one billion pieces of information being updated on a monthly basis. Over 220 million consumers have some form of credit information attached to them, and transactional data is flowing all the time. Fail to update and a furnisher will quickly see flaws in their reporting. In fact, a recent study revealed an estimated 2.1% of contact info goes bad if unattended for more than one month. Clearly, achieving data quality is an ongoing investment for any organization, but companies often lack a clean plan. Some data furnishers fail to report, or elect to report to just one bureau, even though providing better data will result in a more complete and accurate credit profile. So how do you tackle the challenge of data quality? Organizations should consider implementing these six steps: Review data governance. Correct errors in data submissions. Complete an audit of data submissions. Evaluate disputes and resolutions. Compare data to peers and the industry. Review existing policies and processes. Follow these steps and your organization will earn a reputation among both regulators and consumers for clean, credible data. Plus, the investment in better data will reduce the need to resolve future disputes and fines. To learn more about meeting your FCRA responsibilities and best practices around data quality, check out our on-demand webinar or data integrity services site.

It’s official. Millennials have surpassed Baby Boomers in population size, according to the US Census. And while they are quick to adopt the “selfie” and all things social, they have been slow to embrace the world of credit. Sure, there’s been increased regulation over the past decade, and coming into adulthood in the midst of the Great Recession hasn’t helped. But don’t count Millennials out of the credit game just yet. A deeper, more segmented view of this digital-dependent generation shows a very diverse population with plenty of opportunity for lenders. Plus, their sheer size in numbers and $200 billion in annual buying power demand financial institutions evolve to accommodate this massive market. As Gen Y comes of age, there is growing evidence they are open to building and growing their personal credit history. But if financial institutions wish to capture the attention and business of this demographic, they must adapt, leveraging deeper segmentation insights with more effective prospecting strategies to reach them. Experian's data reveals key trends in terms of how this generation is utilizing credit, tips and tools to find the most credit-ready individuals, and strategies to grow the thin-file Millennials as they come of age. “Given the significance millennials play in financial services and the credit marketplace, it is crucial to understand this influential consumer segment and how they use credit as a tool,” said Michele Raneri, vice president of analytics and business development. “While this generation may not look like they are on the right track financially, it’s important to keep in mind that credit scores are built on credit experiences, and while this generation has been slower to use credit, they have plenty of opportunities to build a positive credit history.” To learn more about Millennials and credit, visit Experian.com/millennials.

Customer Experience during the holiday shopping season During the holidays, consumers transact at a much greater rate than any other time of the year. Many risk-management departments respond by loosening the reins on their decision engines to improve the customer experience — and to ensure that this spike does not trigger a response that would impede a holiday shopper’s desire to grab one more stocking stuffer or a gift for a last-minute guest. As a result, it also is the busy season for fraudsters, and they use this act of goodwill toward your customers to improve their criminal enterprise. Ultimately, you are tasked with providing a great customer experience to your real customers while eliminating any synthetic ones. Recent data breaches resulted in large quantities of personally identifiable information that thieves can use to create synthetic identities being published on the Dark Web. As this data is related to real consumers, it can be difficult for your identity-authentication solution to determine that these identities have been compromised or fabricated, enabling fraudsters to open accounts with your organization. Experian’s Identity Element Network™ can help you determine when synthetic identities are at work within your business. It evaluates nearly 300 data-element combinations to determine if certain elements appear in cyberspace frequently or are being used in combination with data not consistent with your customer’s identity. This proven resource helps you manage fraud across the Customer Life Cycle and hinder the damage that identity thieves cause. Identity Element Network examines a vast attribute repository that grows by more than 2 million transactions each day, revealing up-to-date fraud threats associated with inconsistent or high-risk use of personal identity elements. Our goal is to provide the comfort of knowing that you are transacting with your real customers. Don’t get left in the cold this holiday season — fraudsters are looking for opportunities to take advantage of you and your customers. Contact your Experian account executive to learn how Identity Element Network can help make sure you are not letting fraudsters exploit the customer experience intended for your real customers. Learn more about the delicate balance between customer and criminal by viewing our fraud e-book.

Electronic signatures and their emerging presence in our Internet-connected world I had the opportunity to represent Experian at the eSignRecords 2015 conference in New York City last week. The concept of electronic signature, while not new, certainly has an emerging presence in the Internet-connected world — as evidenced by the various attendee companies that were represented, everything from home mortgages to automobiles. Much of the discussion focused on the legal aspects of accepting an electronic signature in lieu of an in-person physical signature. The implications of accepting this virtual stamp of approval were discussed, as well as the various cases that already have been tried in court. Of course, the outcome of those cases shapes the future of how to properly integrate this new form of authorization into existing business processes. Attendees discussed the basic concept of simply accepting a signature on an electronic pad as opposed to one written on a piece of paper. That act alone has many legal challenges even though it provides the luxury of in-person authentication through a face-to-face meeting. The complexities and risk increase exponentially when these services are extended over the Internet. The ability to sign documents virtually opens up a whole new world of business opportunities, and the concept certainly caters to the consumer’s need for convenience. However, the anonymity of the Internet presents the everyday challenge of balancing consumer expectations of greater ease of use with necessary fraud prevention measures. Ultimately, it always comes back to understanding who is actually signing that document. All of this highlights the need for robust authentication and security measures. As more and more legal documents and contracts are passed around virtually, the opportunity to properly screen and verify who has access to the documents gets more critical. Many organizations still rely on the tried-and-true method of knowledge-based authentication (KBA), while many others have called for its end. KBA continues to soldier on as an effective way to ensure that people on the other end of the wire are who they say they are by asking questions that — presumably — only they know the answers to. In most cases, KBA is viewed as a “check the box” step in the process to satisfy the lawyers. In certain cases, that’s all you need to do to ensure compliance with legal policy or regulatory requirements. It starts to get tricky is when there’s more on the line than just “check the box” actions. When the liability of first- or third-party fraud, becomes greater than simple compliance, it’s time to implement tighter security, while at the same time limiting the amount of friction caused by the process. Many in attendance discussed the need for layers of authentication based on the type of documents that are being processed and handled. This speaks directly to the point that one size does not fit all. As the industry matures and acceptance of e-signatures increases, so too does the need for more robust, flexible options in authentication. Another topic — that was quite frankly foreign to everyone we talked to — was the need for security around the concept of account takeover. When discussing this type of fraud, most attendees did not even consider this to be a hole in their strategy. Consider this fictional scenario. I’m responsible for mergers and acquisitions for my publicly traded company. I often share confidential information via electronic means, leveraging one of the many electronic signature solutions on the market. I become a victim of a phishing attack and unknowingly provide my login credentials to the fraudster. The fraudster now has access to every electronic document that I have shared with various organizations — most of which have been targets for mergers and acquisitions. Fraudsters are creative. They exploit new technologies — not because they’re trendsetters, but because oftentimes these new technologies fail to consider how fraudsters can benefit from the system. If you are considering adopting e-signature as a formal process, please consider implementing: Flexible levels of authentication based on the risk and liability of the documents that are being presented and what they are protecting FraudNet for Account Takeover, which enhances security around access to these critical documents to protect against data breaches Not only the needs and experiences of your own business, but customer needs as well to enable to the best possible customer interactions If you haven’t considered implementing e-signature technology into your business process, you should — but be sure to have your fraud team present when considering the implementation.

This month, it’s all about parties and gift giving and holiday traditions. Fast forward a month, however, and consumers will be in a different place. Today, they are spending. In a few weeks, the focus will be on paying down bills, or perhaps seeking solutions to consolidate or transfer balances. The good news for the economy is consumers are expected to spend more this holiday season – $830 on average, a huge jump from last year’s $720. Total retail is expected to increase 5.6 percent, while ecommerce (thanks Amazon Prime) should rise 13.9 percent. Credit card originations are also trending up more than 1 percent year-over-year as of the end of the third quarter of 2015. So what does this mean for lenders? Card utilization is peaking, creating the perfect scenario for many consumers to seek balance transfers, consolidate debt and search for competitive rates, especially if they’ve been leveraging high-interest cards. A recent analysis by NerdWallet revealed consumers are more interested in shopping with store credit cards than with traditional cards this season, putting them at particular risk of sky-high rates. A deeper look at utilization revealed super-prime consumers use less than 6 percent of their available credit limits, while consumers in the deep-subprime tier use nearly every dollar allotted. “Consumers spend billions during the holidays on high-interest credit cards,” said Kyle Matthies, Experian product manager. “Many of them have excellent credit, but struggle juggling multiple payments, which can lead to delinquencies. Credit card consolidation can provide relief by lowering interest rates and simplifying repayment.” Card issuers that remain passive during this window may find their portfolios at-risk as customers take advantage of seasonal offers. Competitors who capitalize on this peak season of balance transfers will likely be mailing out offers to acquire and grow their card portfolio, as well as protect their current card base. “As banks and credit unions finish out the calendar year, they might seek one last marketing push, so a balance-transfer campaign might be the ideal play,” said Matthies. “Still, to avoid blowing the budget, it helps to leverage data to know exactly who to target – both within and outside the card portfolio.” Specific models and/or tools can identify who to try to retain, as well as provide insights on whom to conquest from the outside. An index can additionally offer guidance on when to lower APRs, sweeten rewards and increase credit limits for specific consumers. The post-holiday balance-transfer wave is coming. The question is which lenders will be best prepared to protect and grow their respective card portfolios.

Hello from the other side ... While Adele scores big on the Billboard Hot 100 by crooning of coming to terms with a lover from the past, a new Experian “State of Credit” reveals we are officially on the “other side” of the recession – at least if you’re looking at the nation’s credit scores. While the bottom of the Great Recession was reached in the second quarter of 2009, steady job growth was not seen until 2011, and even since, some economists claim it has been a "Tortoise Recovery.” But key findings from Experian’s 6th annual study, ranking top and bottom cities across the nation in regards to credit, suggests the U.S. is strong. “If I were to give a grade to the overall picture of credit in the United States, I would give it an A minus,” said Michele Raneri, Experian’s vice president of analytics and new business development. “I’m optimistic about the state of credit as we are seeing more loans being extended, late payments are decreasing and consumers are continuing to gain more confidence in originating loans. There definitely is growth and momentum — we’re back to prerecession levels in nearly every category, which means lenders are in a prime position to capitalize on this market and foster business growth.” Which states topped the credit charts? As in previous years, Minnesota continues to shine with three of its cities — Mankato, Rochester and Minneapolis — leading with credit scores of 706, 705 and 704, respectively. Greenwood, Miss. and Albany, Ga. ranked the lowest with scores of 612 and 622. While still at the bottom of the list with a score of 612, Greenwood, Miss., residents did improve their score by three points, more than any other city in the bottom 10. Overall, the report reveals the national credit score increased by three points over the last year (and by five points since 2013) and the 10 cities with the highest credit scores in the nation increased their scores by an average of 1.8 points. Additionally, bankcards, retail cards and mortgage lending showed significant growth, making this year’s study an indicator of the nation’s confidence in the credit market. Just in time for the election year, this year’s study includes insight into how residents of these top and bottom metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs) identify politically. The study found that half of the highest-scoring cities have residents whose views skew more middle of the road, while residents of lower-scoring cities are more likely to lean conservative. The full lists of the top 10 and bottom 10 cities are featured (scores are rounded to the nearest whole number). Detailed study highlights include the following changes over the last year: The national VantageScore® credit score is up by three points, from 666 to 669. Bankcard lending continues to increase, with new bankcards up 7.7 percent. The average number of bankcards per consumer is up 2.8 percent to 2.24 cards. Retail card lending also is on the rise, with a 10.8 percent increase in new originations. The average number of retail cards per consumer is up 0.3 percent to 1.55 cards from last year and up by 7 percent since 2013. Instances of late payments (includes bankcard and retail) decreased by 4.4 percent over the last year and by 17.3 percent since the height of the recession in 2010. Average debt2 is up 2.1 percent to $29,093 per consumer. Mortgage originations increased by 42.5 percent. For a more complete look at the above cities as well as the other MSAs studied, visit http://www.livecreditsmart.com to view a fully interactive map and infographic. Purchase The Experian Market Intelligence Brief, a quarterly report that includes more than 70 charts and data trends on loan originations, outstanding loans and delinquency performance metrics spanning three years.

Profile of an online fraudster I recently read a study about the profile of a cybercriminal. While I appreciate the study itself, one thing it lacks perspective on is an understanding of how identity data is being used to perpetrate fraud in the online channel. One may jump to conclusions about what is a good indicator for catching fraudsters. These very broad-brush observations may result in an overwhelming number of false positives without digging in deeper. Purchase value A single approach for understanding the correlation between purchase value and fraud does not work to best protect all businesses. Back in 2005, we saw that orders under $5 were great indicators of subsequent large-ticket fraud. For merchants that sell large-ticket items, such as electronics, those same rules may not be effective. To simply believe that the low dollar amount is the extent of the crime and not just a precursor to the real, bigger crime indicates a lack of understanding of how fraudsters work to manipulate a system. For some merchants, where fraudsters know they can go to do card testing against their business, low-dollar-amount rules may apply. However, for other businesses a different set of rules must be put into place. Time of day We have been tracking fraud time of day as a rule since 2004, but the critical point is a clear definition of which time of day. For the merchant, 3 a.m. is very different than 3 a.m. for a fraudster who is in Asia or Eastern Europe, where 3 a.m. merchant time is actually the middle of the online fraudster’s day. FraudNet is designed to identify the time from the user’s device and runs its rules from the user’s time. We find that every individual business will have a very specific threat profile. Businesses need to build their individual fraud strategy around their overall attack rate taking into account the strength of the defense and the ability to be flexible to accommodate the nuances for individual consumers. A general approach to fraud mitigation inevitably results in a system that begins to chase broad averages, which leads to excessive false positives and mediocre detection. That’s what drives us to do the job better. The proof of every fraud solution should lie in its ability to catch the most fraud without negatively impacting good customers.

Understanding the Impact of New Marketplace Lending Regulations The online marketplace lending sector has enjoyed unprecedented growth these past few years. According to a recent Morgan Stanley research report, the volume of loans extended by online marketplace lenders in the United States has doubled every year since 2010, hitting $12 billion last year. Some analysts speculate this growth will continue at a compound annual rate of 47 percent through 2020. The market’s growth, coupled with new, disruptive lending models, is now prompting regulators in Washington to raise questions about the potential opportunities and challenges for consumers, small businesses, and the safety and soundness of our financial system. Last July, the Treasury Department issued a request for information to better understand the benefits and risks associated with new online lending platforms and other “fin-tech” startups. The Treasury’s RFI sought information about how these entities’ business models differ from traditional lenders, their impact on financially underserved consumers, and ultimately whether the regulatory framework should evolve to ensure the safe growth of this emerging marketplace. They were also interested in how online lenders were assessing credit risk of borrowers. Most comments the Treasury Department received from online lenders focused on the positive impact that innovation in financial services could have on consumers and small businesses. For example, in an open letter to the Treasury, Lending Club Founder and CEO Renaud Laplanche stated his company’s role in “bringing more transparency, removing friction, reducing systemic risk by requiring a match between assets and liabilities, and offering traditional banks … the opportunity to participate on our platform and benefit from the same cost reductions from which our other borrowers and investors benefit.” Laplanche emphasized the benefits to consumers by noting that “over 70 percent of borrowers on our platform report using their loan to pay off an existing loan or credit card balance and report that the interest rate on their Lending Club loan was an average of seven percentage points lower than they were paying on their outstanding debt or credit cards.” For small businesses, Laplanche explained how commercial loans less than $250,000 tend to be underserved by traditional lenders. “Bank loans from $100k to $250k have fallen 22 percent since 2007, during a period when bank loans of $1 million or greater increased by 56 percent,” he wrote. “Our platform’s automated processes allow us to provide smaller commercial loans that are less available more economically than traditional banks can.” Meanwhile, some commenters called for regulators to increase oversight of the marketplace to provide more certainty. In a joint comment letter, the American Bankers Association and Consumer Bankers Association argued that all lenders — regardless of medium by which they deliver loans — should operate under the same rules and standards. They highlighted the numerous consumer protections in place to protect borrowers — from transparency in pricing, to fair debt collection methods, and data protection — and advocate for these protections to apply in all bank-like activities involving lending or servicing. But what about the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)? The CFPB will take a leadership role to ensure marketplace lenders comply with the fair lending and consumer financial protection laws that the CFPB has authority to enforce. The CFPB has not made any direct notice to the online lending marketplace specifically, but it did issue a notice in October 2014 saying it had no intention of bringing enforcement actions against companies that offer innovative financial products — so long as they benefit consumers. Meanwhile, it is also likely the Federal Trade Commission and state attorneys general will increase their focus on the online lending segment, especially as it relates to how products and services are marketed. The FTC held a symposium on Oct. 30 to examine online lead generation and consumer protection in the lending and education industries. The FTC workshop raised questions about the potential consumer protection challenges of this advertising medium used heavily by online lenders. In particular, there were calls for greater transparency in the use of lead generation, including more information on the ways consumer data is collected through lead-gen websites and how it is used and shared. Online marketplace lenders should expect to stay under the regulatory spotlight – because that’s what success often brings. The sector can avoid undue burdens by ensuring compliance with existing laws and adopting and following industry best practices. For more information, visit www.experian.com/marketplacelending.

What the EMV Shift means for you I recently facilitated a Webinar looking at myths and truths in the market regarding the EMV liability shift and what it means for both merchants and issuers. I found it to be a very beneficial discussion and wanted to take some time to share some highlights from our panel with all of you. Of course, if you prefer to hear it firsthand, you can download the archive recording here. Myth #1: Oct. 1 will change everything Similar to the hype we heard prior to Y2K, Oct. 1, 2015, came and went without too much fanfare. The date was only the first step in our long and gradual path to EMV adoption. This complex, fragmented U.S. migration includes: More than 1 billion payment cards More than 12 million POS terminals Four credit card networks Eighteen debit networks More than 12,000 financial institutions Unlike the shift in the United Kingdom, the U.S. migration does not have government backing and support. This causes additional fragmentation and complexity that we, as the payments industry, are forced to navigate ourselves. Aite Group predicts that by the end of 2015, 70 percent of U.S. credit cards will have EMV capabilities and 40 percent of debit cards will be upgraded. So while Oct. 1 may not have changed everything, it was the start of a long and gradual migration. Myth #2: Subscription revenues will plummet due to reissuances According to Aite, EMV reissuance is less impactful to merchant revenues than database breaches, since many EMV cards are being reissued with the same pan. The impact of EMV on reoccurring transactions is exaggerated in the market, especially when you look at the Update Issuer provided by the transaction networks. There still will be an impact on merchants, coming right at the start of the holiday shopping season. The need for consumer education will fall primarily on merchants, given longer lines at checkout and unfamiliar processes for consumers. Merchants should be prepared for charge-back amounts on their statements, which they aren’t used to seeing. Lastly, with a disparate credit and debit user experience, training is needed not just for consumers, but also for frontline cashiers. We do expect to see some merchants decide to wait until after the first of the year to avoid impacting the customer experience during the critical holiday shopping season, preferring to absorb the fraud in the interest of maximizing consumer throughout. Myth #3: Card fraud will decline dramatically We can look to countries that already have migrated to see that card fraud will not, as a whole, decline dramatically. While EMV is very effective at bringing down counterfeit card fraud, organized crime rings will not sit idly by while their $3 billion business disappears. With the Canadian shift, we saw a decrease in counterfeit card loss but a substantial increase in Card Not Present (CNP) fraud. In Canada and Australia, we also saw a dramatic, threefold increase in fraudulent applications. When criminals can no longer get counterfeit cards, they use synthetic and stolen identities to gain access to new, legitimate cards. In the United States, we should plan for increased account-takeover attacks, i.e., criminals using compromised credentials for fraudulent CNP purchases. For merchants that don’t require CVV2, compromised data from recent breaches can be used easily in an online environment. According to Aite, issuers already are reporting an increase in CNP fraud. Fraudsters did not wait until the Oct. 1 shift to adjust their practices. Myth #4: All liability moves to the issuer EMV won’t help online merchants at all. Fraud will shift to the CNP channel, and merchants will be completely responsible for the fraud that occurs there. We put together a matrix to illustrate where actual liability shifts and where it does not. Payments liability matrix Note: Because of the cost and complexity of replacing POS machines, gas stations are not liable until October 2017. For more information, or if you’d like to hear the full discussion, click here to view the archive recording, which includes a great panel question-and-answer session.
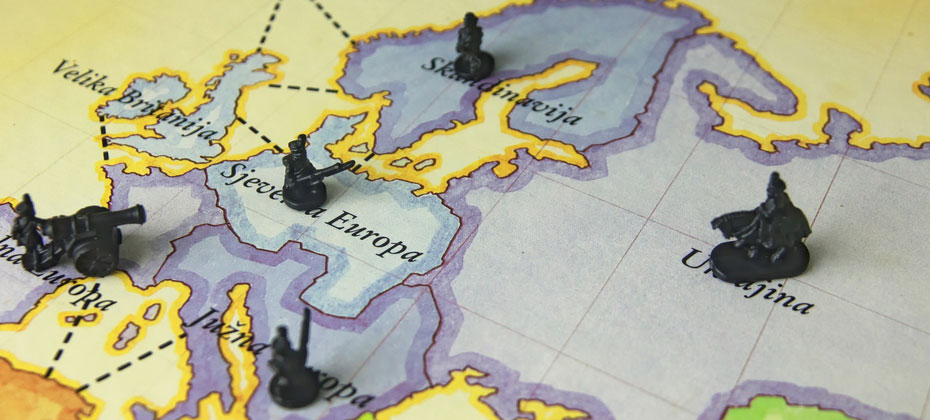
While walking through a toy store in search of the perfect gift for a nephew, I noticed the board game Risk, which touts itself as “The Game of Global Domination.” For those who are unaware, the game usually is won by players who focus on four key themes: Strategy — Before you begin the game, you need a strategy to attack new territories while defending your own Attack — While you have the option to sit back and defend your territory, it’s better to attack a weakened opponent Fortify — When you are finished attacking, it’s often best to fortify your position Alliances — While not an official part of the game, creating partnerships is necessary in order to win These themes also are relevant to the world of real-life fraud risk prevention. The difference is that the stakes are real and much higher. Let’s look at how these themes play out in real-life fraud risk prevention: Strategy — Like in the game, you need a strategy for fraud risk detection and prevention. That strategy must be flexible and adaptable since fraudsters (your enemies) also continuously adapt to changing environments, usually at a much quicker, less bureaucratic pace. For example, your competitors (other countries) may improve their defenses, so fraudsters will mount a more focused attack on you. Fraudsters also may build alliances to attack you from different vectors or channels, resulting in a more sophisticated, comprehensive strike. Attack — As the game begins, all players have access to all competitors (countries). This means that fraudsters might have the upper hand in a certain area of the business. You can sit back and try to defend the territory you already “own,” where fraudsters have no traction, but it’s best to be aggressive and attack fraudsters by expanding your coverage across all channels. For example, you might have plenty of controls in place to manage your Web orders (occupied territory), but your call center operations (opponents’ territory) aren’t protected, i.e., the fraudsters “own” this space. You need to attack that channel to drive fraudsters out. Fortify — In the game, you can fortify your position after a successful move — that is, move more troops to your newly conquered territories. In real life, you always have the option to fortify your position, and you should constantly look for ways to improve your controls. You can’t afford to maintain on your current position, because fraudsters constantly are looking for weaknesses. Alliances — In business, we often are hesitant to share information with our competitors. Fraudsters use this to their advantage. Just as fraudsters act in a coordinated fashion, so must we. Use all available resources and partners to shore up your defenses Leverage the power of consortium data Learn new methods from traditional competitors Always team up with internal and external partners to defend your territory If you apply these themes, you will be positioned for global domination in the fight against fraud risk. You can read more about fraud-prevention strategies in our recent ebook, Protecting the Customer Experience. As a side note, I’m always ready for a game of Risk, so contact me if you’re interested. But be forewarned — I’m competitive.

What will the EMV shift really mean for consumers and businesses here in the U.S.? Businesses and consumers across the U.S. are still adjusting to their new EMV credit cards. The new credit cards are outfitted with computer chips in addition to the magnetic strips to help prevent point-of-sale (POS) fraud. The new system, called EMV (which stands for Europay, MasterCard and Visa), requires signatures for all transactions. EMV is a global standard for credit cards. In the wake of the rising flood of large-scale data breaches at major retailers – and higher rates of counterfeit credit card fraud – chip-and-signature, as it is also called, is designed to better authenticate credit card transactions. Chip-and-signature itself is not new. It has been protecting consumers and businesses in Europe for several years and now the U.S. is finally catching up. But what will the EMV system really mean for consumers and businesses here in the U.S.? There is the potential for businesses that sell both offline and online, to see an increase in fraud that takes place online called Card Not Present (CNP) fraud. Will credit card fraud ever really be wiped out? Can we all stop worrying that large-scale point-of-sale breaches will happen again? Will the EMV shift affect holiday shopping and should retailers be concerned? Join us as we explore these questions and more on an upcoming Webinar, Chipping Away at EMV Myths. Our panel of experts includes: David Britton, Vice President, Industry Solutions, Experian Julie Conroy, Research Director, Aite Group Mike Klumpp, Director of Fraud Prevention, Citibank Moderated by: Keir Breitenfeld, Vice President, Product Management, Experian