The gig economy — also called the sharing economy or access economy — is an activity where people earn income by providing on-demand work, services, or goods. Often, it is through a digital platform like an application (app) or website.
The gig economy seamlessly connects individuals with a diverse range of services, whether it be a skilled handyman for those long-awaited office shelves, or an experienced chauffeur to quickly drive you to the airport to not miss your flight. However, there are instances when these arrangements fall short of expectations. The hired handyman may send a substitute who’s ill-equipped for the task, or the experienced driver takes the wrong shortcut leaving you scrambling to make your flight on time. On the flip side, there are numerous risks faced by those working in the gig/sharing economy, from irritable customers to dangerous situations. In such cases, trust takes a hit.
The gig economy has witnessed a surge in recent years, as individuals gravitate towards flexible, freelance, and contract work instead of traditional full-time employment. This shift has unlocked a multitude of opportunities for both workers and businesses. Nevertheless, it has also ushered in challenges pertaining to security and trust. One such challenge revolves around the escalating significance of digital identity verification within the gig economy.
Digital identity verification and the gig economy
Digital identity verification encompasses validating a person’s identity through digital means, such as biometric data, facial recognition, or document verification. Within the gig economy, this process has high importance, as it establishes trust between businesses and their pool of freelance or contract workers. With the escalating number of remote workers and the proliferation of online platforms connecting businesses with gig workers, verifying the identities of these individuals has become more vital than ever before.
Protecting gig users and improving the customer experience
One primary rationale behind the mounting importance of digital identity verification in the gig economy is its role in curbing fraud. As the gig economy gains traction, the risk of individuals misrepresenting themselves or their qualifications to secure work burgeons. This scenario can lead businesses to hire unqualified or even fraudulent workers, thereby posing severe repercussions for both the company and its customers. By adopting digital identity verification processes, businesses can ensure the legitimacy and competence of their workforce, subsequently decreasing the risk of fraudulent activities.
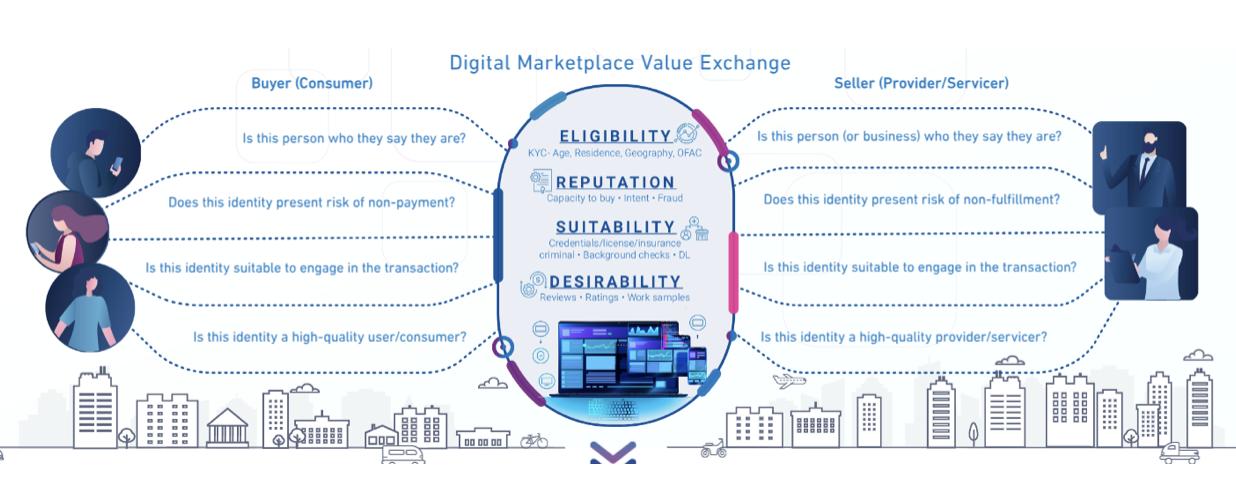
In the digital age, trust and safety are crucial for businesses to succeed. Consumers prioritize brands they can trust, and broken trust can lead to loss of customers.
According to Experian’s 2023 Fraud and Identity Report, over 52% of US consumers feel they’re more of a target for online fraud than they were a year ago. As such, online security continues to be a real concern for most consumers. Nearly 64% of consumers say that they are very or somewhat concerned with online security, with 32% saying they are very concerned. Establishing trust and safety measures not only protects your brand but also enhances the user experience, fosters loyalty, and boosts your business.
Role of a dedicated Trust and safety team
Trust and safety are the set of business practices for online platforms to follow to reduce the risk of users being exposed to harm, fraud, or other behaviors outside community guidelines. This is becoming an increasingly important function as online platforms look to protect their users while improving customer acquisition, engagement, and retention.
That team also safeguards organizations from security threats and scams. They verify customers’ identities, evaluate actions and intentions, and ensure a safe environment for all platform users. This enables both organizations and customers to trust each other and have confidence in the platform. Their role has evolved from fraud prevention to encompass broader areas, such as user-generated content and the metaverse. With the rise of user-generated content, platforms face challenges like fake accounts, imitations, malicious links, and inappropriate content. As a result, trust and safety teams have expanded their focus and are involved in product engineering and customer journey design.
Another noteworthy factor contributing to the growing emphasis on digital identity verification for trust and safety teams stems from the necessity to adhere to diverse regulations and laws. Many countries have implemented stringent regulations to safeguard workers and ensure the legal and ethical operations of businesses. In the United States, for instance, businesses must verify the identities and work eligibility of all employees, including freelancers and contractors, as part of the Form I-9 process. By leveraging digital identity verification tools, businesses can streamline these procedures and guarantee compliance with prevailing regulations.
Mitigating risk in online marketplaces
To mitigate risks in online marketplaces, businesses can take several steps, including creating a clear set of user guidelines, implementing identity verification during onboarding, enforcing multi-factor authentication for all accounts, leveraging reverification during high-risk moments, performing link analysis on the user base, and applying automation.
Online identity verification plays a pivotal role in safeguarding gig workers themselves. With the surge of online platforms connecting businesses with freelancers and contractors, there comes an augmented risk of workers falling prey to scams or identity theft. By mandating digital identity verification as an integral part of the onboarding process, these platforms can shield workers and ensure they only engage with bona fide businesses.
While automation can be a powerful tool for fraud detection and mitigation, it is not a cure-all solution. Automated identity verification has its strengths, but it also has its weaknesses. While automation can spot risk signals that a human might miss, a human might spot risk signals that automation would have skipped. Therefore, for many companies, the goal should not be full automation but achieving the right ratio of automation to manual review. Manual review takes time, but it’s necessary to ensure that all potential risks are identified and addressed. The more efficient these processes can be, the better, as it allows for a quicker response to potential threats.
As the number of individuals embracing freelance and contract work surges, and businesses increasingly rely on these workers to carry out vital responsibilities, ensuring the security and trustworthiness of these individuals becomes paramount. By integrating digital identity verification processes, businesses can shield themselves against fraud, comply with regulations, and cultivate trust with their gig workers.
Finding the right partner
While trust and safety are concerns for all online marketplaces, there’s no universal solution that will apply to all businesses and in all cases. Your trust and safety policies need to be tailored to the realities of your business. The industries you serve, regions you operate in, regulations you are subject to, and expectations of your users should all inform your processes. Experian’s comprehensive suite of customizable identity verification solutions can help you solve the problem of trust and safety once and for all.
*This article leverages/includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information.


