660 Credit Score: Is it Good or Bad?
A FICO® ScoreΘ of 660 places you within a population of consumers whose credit may be seen as Fair. Your 660 FICO® Score is lower than the average U.S. credit score.
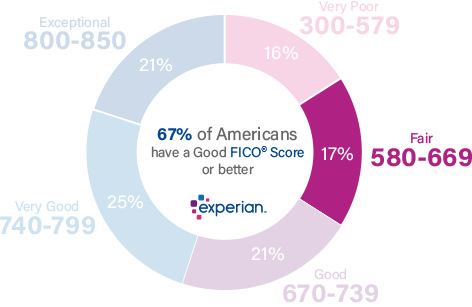
17% of all consumers have Scores in the Fair range (580-669).
Statistically speaking, 28% of consumers with credit scores in the Fair range are likely to become seriously delinquent in the future.
Some lenders dislike those odds and choose not to work with individuals whose FICO® Scores fall within this range. Lenders focused on "subprime" borrowers, on the other hand, may seek out consumers with scores in the Fair range, but they typically charge high fees and steep interest rates. Consumers with FICO® Scores in the good range (670-739) or higher are generally offered significantly better borrowing terms.
How to improve your 660 Credit Score
The average FICO® Score is 714, somewhat higher than your score of 660, which means you've got a great opportunity to improve.
76% of U.S. consumers' FICO® Scores are higher than 660.
What's more, your score of 660 is very close to the Good credit score range of 670-739. With some work, you may be able to reach (and even exceed) that score range, which could mean access to a greater range of credit and loans, at better interest rates.
The best approach to improving your credit score starts with a check of your FICO® Score. The report that's delivered with the score will use details from your unique credit report to suggest ways you can increase your score. If you focus on the issues spelled out in the report and adopt habits that promote good credit scores, you may see steady score improvements, and the broader access to credit that often comes with them.
Moving past a Fair credit score
While everyone with a FICO® Score of 660 gets there by his or her own unique path, people with scores in the Fair range often have experienced credit-management challenges.
The credit reports of 72% of Americans with a FICO® Score of 660 include at least one late payment 30 or more days past due.
Credit reports of individuals with Fair credit cores in the Fair range often list late payments (30 days or more past due) and collections accounts, which indicate a creditor has given up trying to recover an unpaid debt and sold the obligation to a third-party collections agent.
Some people with FICO® Scores in the Fair category may even have major negative events on their credit reports, such as foreclosures or bankruptcies—events that severely lower scores. Full recovery from these setbacks can take up to 10 years, but you can take steps now to get your score moving in the right direction.
Studying the report that accompanies your FICO® Score can help you identify the events that lowered your score. If you correct the behaviors that led to those events, work steadily to improve your credit, you can lay the groundwork to build up a better credit score.
What’s in a credit score?
Credit scores such as the FICO® Score are based on your debt-management history, as recorded in your credit file. The scores are basically a summation of the way you've handled credit and bill payment. Good credit habits tend to promote higher credit scores, while poor or erratic habits tend to bring lower scores.
Here's a more detailed breakdown of the specific factors that influence your FICO® Score:
Public Information: If bankruptcies or other public records appear on your credit report, they can have severe negative impacts on your credit score.
Among consumers with a FICO® Score of 660, the average credit card debt is $6,554.
Payment history. Delinquent accounts and late or missed payments can harm your credit score. A history of paying your bills on time will help your credit score. It's pretty straightforward, and it's the single biggest influence on your credit score, accounting for as much as 35% of your FICO® Score.
Credit usage rate. To determine your credit utilization ratio, add up the balances on your revolving credit accounts (such as credit cards) and divide the result by your total credit limit. If you owe $4,000 on your credit cards and have a total credit limit of $10,000, for instance, your credit utilization rate is 40%. You probably know your credit score will suffer if you "max out" your credit limit by pushing utilization toward 100%, but you may not know that most experts recommend keeping your utilization ratio below 30% to avoid lowering your credit scores. Credit usage is responsible for about 30% of your FICO® Score.
Length of credit history. Credit scores generally benefit from longer credit histories. There's not much new credit users can do about that, except avoid bad habits and work to establish a track record of timely payments and good credit decisions. Length of credit history can constitute up to 15% of your FICO® Score.
Total debt and credit. Credit scores reflect your total amount of outstanding debt you have, and the types of credit you use. The FICO® Score tends to favor a variety of credit, including both installment loans (i.e., loans with fixed payments and a set repayment schedule, such as mortgages and car loans) and revolving credit (i.e., accounts such as credit cards that let you borrow within a specific credit limit and repay using variable payments). Credit mix can influence up to 10% of your FICO® Score.
Recent applications. When you apply for a loan or credit card, you trigger a process known as a hard inquiry, in which the lender requests your credit score (and often your credit report as well). A hard inquiry typically has a short-term negative effect on your credit score. As long as you continue to make timely payments, your credit score typically rebounds quickly from the effects of hard inquiries. (Checking your own credit is a soft inquiry and does not impact your credit score.) Recent credit applications can account for up to 10% of your FICO® Score.
Improving Your Credit Score
Fair credit scores can't be turned into exceptional ones overnight, and only the passage of time can repair some negative issues that contribute to Fair credit scores, such as bankruptcy and foreclosure. No matter the reason for your Fair score, you can start immediately to improve the ways you handle credit, which can lead in turn to credit-score improvements.
Look into obtaining a secured credit card. A secured credit card requires you to put down a deposit in the full amount of your spending limit—typically a few hundred dollars. Confirm that the As you use the card and make regular payments, the lender reports your activity to the national credit bureaus, where they are recorded in your credit files. (Making timely payments and avoiding "maxing out" the card will favor credit-score improvements.
Consider a credit-builder loan. Available from many credit unions, these loans take can several forms, but all are designed to help improve personal credit histories. In one popular version, the credit union places the money you borrow in a savings account, where it earns interest but is inaccessible to you until the loan is paid off. Once you've paid the loan in full, you get access to the funds and the accumulated interest. It's a clever savings tool, but the credit union also reports your payments to national credit bureaus, so regular, on-time payments can lead to credit-score improvements. (Check before taking out a loan to make sure the lender reports to all three national credit bureaus.)
Consider a debt-management plan. For families with finances stretched too thin to keep up with debt payments, a debt-management plan (DMP) can bring much-needed relief. Getting one requires you to work with a qualified credit counseling agency, who negotiates with your creditors to set up a workable repayment plan. It's a serious step that significantly lowers your credit score and effectively closes all your credit accounts, but it's less severe than bankruptcy, and it can help families in dires straits get back on their feet. Even if you decide a DMP isn't for you, meeting with a credit counselor (not a credit-repair company) may give you some new tools for building up your credit.
Pay your bills on time. Late and missed payments hurt credit scores, so avoid them. Take advantage of automatic payments, calendar alarms, and other automated tools—or just use sticky notes and a paper calendar. Do whatever you can to help you remember, and you'll soon take on good habits that favor credit-score improvements.
Avoid high credit utilization rates. High credit utilization, or debt usage. The FICO® scoring system bases about 30% of your credit score on this measurement—the percentage of your available credit limit represented by your outstanding payment balances. Try to keep your utilization across all your accounts below about 30% to avoid lowering your score.
Among consumers with FICO® credit scores of 660, the average utilization rate is 47.9%.
Try to establish a solid credit mix. You shouldn’t take on debt you don’t need, but prudent borrowing, including a combination of revolving credit and installment debt, can be beneficial to your credit score.
Learn more about your credit score
A 660 FICO® Score is a good starting point for building a better credit score. Boosting your score into the good range could help you gain access to more credit options, lower interest rates, and reduced fees. You can begin by getting your free credit report from Experian and checking your credit score to find out the specific factors that impact your score the most. Read more about score ranges and what a good credit score is.