What Credit Score Do You Start With?
Quick Answer
Your credit score doesn’t start at zero; it doesn’t exist until you begin building credit. While you can’t predict what your first credit score will be, you can take steps to build a good credit history and improve your credit score going forward.

Your credit score is a three-digit number that reflects how you manage credit. Curious what your credit score will be when you're just starting out—say, applying for your first credit card or apartment? Starting with no credit score doesn't mean you start at zero; it just means no credit report exists in your name yet, so there's no data to use to calculate a credit score. Here's how to establish a credit history and become scoreable.
Does Your Credit Score Start at Zero?
Your credit score doesn't start at zero. Instead, your credit score doesn't exist at all until a lender, credit card issuer or other entity requests it to check your creditworthiness. When that happens, information in your credit report is used to calculate your credit score.
If you don't have a credit history, there's no information in your credit report, so there's no score at all. This is called being credit invisible.
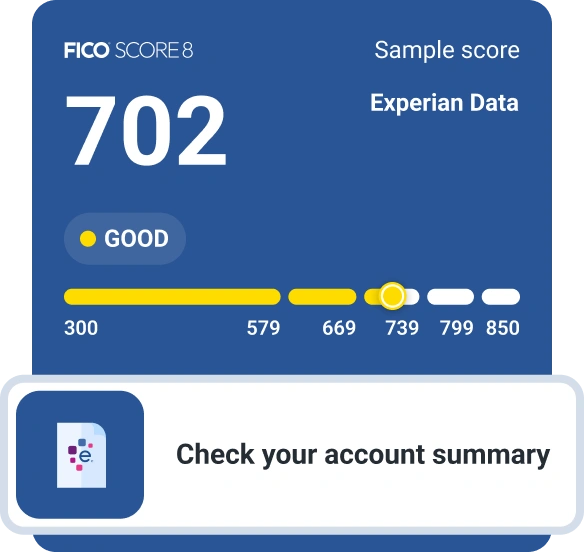
Once you begin establishing a credit history, you might think your credit score will start at 300 (the lowest possible score in most cases). But unless you start out with very poor credit habits, your first credit score probably won't be that low.
Your credit score won't start at the highest level, either, no matter how well you manage your credit to start. Under the two most commonly used credit scoring models, the FICO® ScoreΘ and VantageScore®, the highest possible base credit score is 850. When you're new to credit, you don't have a long enough credit history to earn that perfect score.
Your first credit score will probably fall somewhere between the two extremes.
Learn more:What Are the Different Credit Score Ranges?
When Do You Get a Credit Score?
It generally takes at least six months to establish a credit score, but it could take less time depending on the credit scoring model that is used.
- FICO® Score: To be scoreable by FICO, you must have a credit account at least six months old that reports to at least one of the three major consumer credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion and Equifax). Your credit report must also show activity on a credit account (not necessarily the same one) within the past six months.
- VantageScore: You may be scoreable by VantageScore, the other major credit scoring company, much sooner. VantageScore may be able to generate a credit score as soon as your credit report lists one credit account, even if that account is less than six months old.
Getting a credit score is only the beginning, though. If you have fewer than five credit accounts, also known as a thin credit file, there's not a lot of data for credit scoring models to work with. As you add more credit accounts to your credit report and demonstrate responsible credit usage, you'll build a solid credit history, but achieving excellent credit can take several years.
Learn more:How Long Does It Take to Build a Good Credit Score?
How Is Your Credit Score Calculated?
Your credit score is calculated using five factors: payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, credit mix and new credit accounts. Here's a quick look at each.
- Payment history: Whether or not you pay bills on time is the single most important factor in your credit score. Payment history accounts for 35% of your FICO® Score, which is why you should be careful not to miss a payment.
- Amounts owed: The amounts you owe on all your credit accounts and, importantly, your credit utilization, account for 30% of your FICO® Score. Credit utilization reflects how much of your available credit you're using on revolving credit accounts such as credit cards. To calculate your credit utilization ratio, divide your total credit card balances by your total credit limits and multiply by 100 to get a percentage. Aim to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30% both overall and on each credit account; the lower you can keep it, the better for your scores.
- Length of credit history: How long you've used credit accounts for 15% of your FICO® Score. This calculation considers the age of each account on your credit report and the average age of all your open accounts. A longer credit history generally translates into a higher credit score because it provides more information about your use of credit.
- Credit mix: Responsibly managing both revolving and installment credit accounts can help your credit score. Revolving credit, such as credit cards, allows you to spend up to a certain credit limit and either pay the balance in full each month or carry it over as long as you make a minimum payment. With installment credit, such as car loans and student loans, you borrow a set amount and pay it back in fixed monthly payments by a specific date. Credit mix accounts for 10% of your FICO® Score.
- New credit: The number of new credit accounts you've recently opened, as well as the number of hard inquiries on your credit report, accounts for 10% of your credit score. A hard inquiry occurs when you apply for credit and a lender reviews your credit report. Multiple hard inquiries within a short time indicate greater risk and can hurt your credit score.
How to Check Your Credit Score
You can check your credit score by getting your FICO® Score for free from Experian. You may also be able to get a free credit score from the other credit bureaus, free credit score websites, your bank, or credit card issuers or lenders with whom you have accounts.
Keep in mind that although FICO® Scores are used by 90% of top lenders, there are other models out there. When you check your credit score, it may vary depending on which model the source uses.
Tip: Your credit scores are updated when you request them, and they will reflect new information being sent to the credit bureaus. This could mean your credit score can vary from day to day, or even hour to hour, so don't get too concerned if you see slight shifts in your credit score if you're checking it regularly.
Learn more:Why Are My Credit Scores Different?
How to Build and Maintain a Good Credit Score
Once you have a credit score, you can use credit cards and loans to build a credit history and improve your credit score.
Use Credit Cards Responsibly
If you already have a credit card or two, be sure to pay the bills on time and keep your credit utilization low. Putting a small purchase on a credit card each month (such as a streaming subscription) and paying the balance in full and on time can be an easy way to begin building your credit history.
If you can't qualify for a general credit card because you lack a credit history, consider these options:
- Become an authorized user on a family member's credit card. Choose someone who has good credit and manages their card responsibly. You'll get your own card to use; after a month or two, it will appear on your credit report, where its payment history can benefit your credit score.
- Apply for a secured credit card. Secured cards require putting down a refundable deposit, which typically becomes your credit limit. The deposit does not cover monthly payments, so be sure to make them on time. Once you have a history of timely payments, the issuer may switch you to a regular, unsecured credit card.
- Consider getting a store credit card. These cards can be used at a specific retailer and are typically easier to get than general credit cards. However, retail credit cards typically have high interest rates, so be careful to pay your balance in full each month.
Both retail and secured credit cards usually have low credit limits, so monitor your balances and credit utilization rate closely. Making more than one payment a month can help ensure your credit utilization stays well below 30%.
Tip: Once you've had a credit card for at least six months and your credit score has improved, see if you can apply to increase your credit limit. A higher credit limit makes it easier to keep your credit utilization rate down. However, only do so if you're confident the increased limit won't tempt you to spend more and possibly increase your debt.
Make Loan Payments on Time
One of the easiest ways to build credit is to make all your loan payments on time. If you have student loans, a car loan or a personal loan, demonstrating responsible credit use with timely payments can have a big impact on your scores over time. If you need to apply for a loan but have trouble qualifying for good loan terms on your own, consider asking a family member with good credit to cosign on the loan with you.
If you don't need or want an auto or personal loan, consider a credit-builder loan. Designed to help people improve or establish credit, credit-builder loans are offered by some online lenders, small banks and credit unions.
Credit-builder loans typically come in amounts ranging from $300 to $1,000. The lender puts the money you borrow into a savings account and reports your payments to the credit bureaus. When your loan is paid off at the end of the loan term, which typically ranges from six to 24 months, you receive the balance in the savings account, possibly with interest. Be sure the lender reports payments to all three credit bureaus (not all do) to get the most benefit.
Tip: To help prevent late payments that can hurt your credit score, consider setting up automatic payments on your loans and credit cards. Just make sure you have enough money in your account to cover the payments when they're due.
Learn more:How to Improve Your Payment History
Start Your Credit Journey
Your credit score can affect your ability to qualify for loans and credit cards, rent an apartment or even get a job, so it's important to start your credit journey off on the right foot. Experian offers resources and tools to help, including Experian Go™, a free program that establishes your Experian credit profile and guides you step by step through the process of building credit.
Non-debt payments like rent, utility, phone, insurance and streaming services typically don't appear on your credit report and don't impact your credit score. However, Experian Boost®ø lets you add eligible on-time payments for these household bills to your Experian credit report. This free feature of your Experian account gives you credit for payments you're already making, which could quickly increase your FICO® Scores.
What makes a good credit score?
Learn what it takes to achieve a good credit score. Review your FICO® Score for free and see what’s helping and hurting your score.
Get your FICO® ScoreNo credit card required
About the author
Karen Axelton is Experian’s in-house senior personal finance writer. She has over 20 years of experience as a journalist and has written or ghostwritten content for a variety of financial services companies.
Read more from Karen