
Welcome to the Experian Thought Leadership Hub
Gain insights into the fast-changing world of consumer and business data through our extensive library of resources.
56 resultsPage 1
 Video
Video
As the U.S. economy continues to recalibrate post-pandemic, the transportation and warehousing segments of the logistics sector are signaling caution. While the broader logistics industry has remained in expansion mode, Experian’s latest Commercial Pulse Report reveals that delinquencies are rising—an early warning of growing risk in two of the economy’s most critical subsectors.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Video
Video
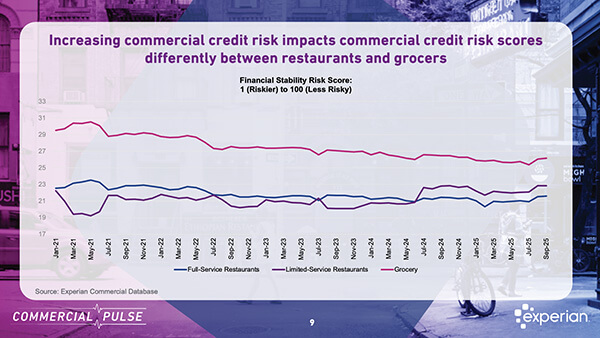
Experian’s latest Commercial Pulse Report dives into the financial health of the restaurant sector amid rising costs and shifting consumer behavior.
Key insights:
What does this mean for lenders and decision makers?
✅ Not all restaurant types face the same risks.
✅ Segmenting credit strategies is more important than ever.
✅ Watch utilization and inquiry trends closely — they may be early indicators of distress.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Video
Video
The construction industry has experienced significant growth over the last seven years, but fresh data reveals mounting signs of financial stress that commercial lenders and Chief Risk Officers should be closely monitoring.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Video
Video
According to Experian’s latest Commercial Pulse Report, business formation remains strong:
What’s driving this resilience?
👉 Faster tech adoption
👉 Hybrid business models
👉 Stronger financial fundamentals
The pandemic forced small businesses to transform at record speed. Now, they’re leveraging those lessons to build smarter, more adaptable enterprises.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Webinar
Webinar
Experian’s Brodie Oldham, VP of Commercial Data Science, and Marsha Silverman, Strategic Analytic Consultant revealed several insights on how small businesses are performing during the Q2 Quarterly Business Credit Review.
During the webinar we asked the audience:
 Video
Video
Outstanding student loan debt in the U.S. has reached an all-time high of $1.63 trillion, and the ripple effects are being felt far beyond the personal finance arena. This unprecedented debt burden is now shaping the way many small business owners borrow, manage credit, and maintain financial stability.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Report
Report
U.S. small businesses are demonstrating exceptional adaptability amid a complex post-pandemic economic environment. Inflation remains elevated above 3%, interest rates are steady between 4.25% and 4.50%, and global trade dynamics continue to introduce volatility. Despite these pressures, small firms are showing resilience, driven by improved digital capabilities, disciplined fiscal management, and a steady flow of entrepreneurial activity.
In Q2 2025, an average of 447,000 new business applications were filed, with significant contributions from minority and younger founders. The Experian Small Business Index™ held steady, credit conditions remained tight. Traditional lenders continued to restrict approvals, with just 13% of applications approved by large banks. In response, small businesses increasingly turned to fintech and embedded finance solutions for faster, data-driven access to capital.
Borrowing behaviors are shifting. The average small business credit card APRs now exceed 25%, firms are transitioning toward installment loans that offer structured repayment terms.
 Video
Video
As temperatures rise across the U.S., so does the nation’s appetite for travel—and the Leisure & Hospitality sector is feeling the heat. In this week’s Commercial Pulse Report, we examine how soaring consumer demand intersects with evolving credit conditions for businesses in travel, lodging, and transportation.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!
 Video
Video
As the automotive sector adapts to rising vehicle prices, shifting consumer behavior, and persistent inflation, the ripple effects are clearly visible in commercial credit activity. Experian’s latest Commercial Pulse Report (July 22, 2025) dives deep into the evolving credit dynamics within the auto industry—and one trend is clear: credit access is contracting across nearly every segment.
Check out the full report to see how these trends could impact your strategy!