What Is a Good Credit Score?
Quick Answer
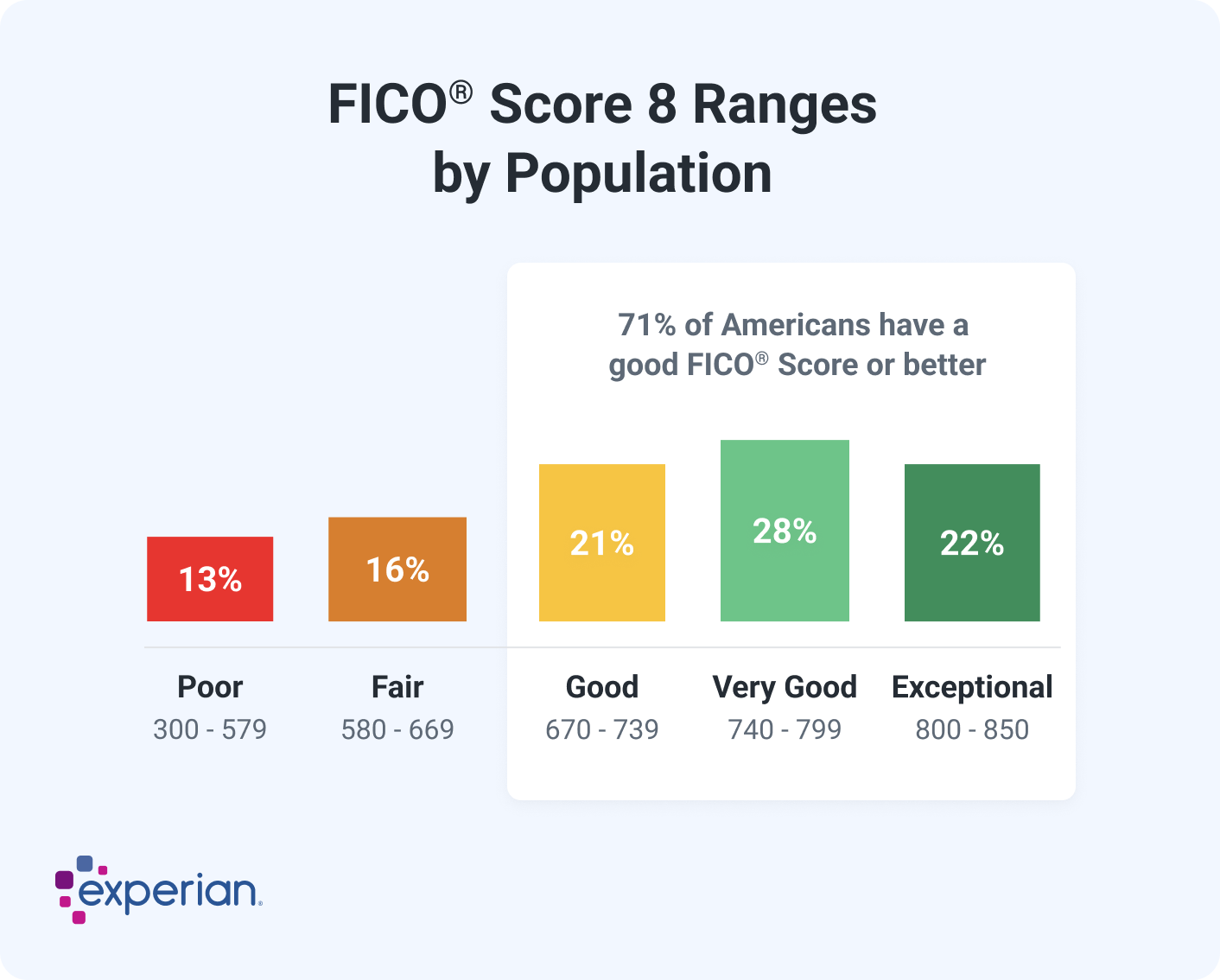
For a score with a range of 300 to 850, a credit score of 670 to 739 is considered good. Credit scores of 740 and above are very good while 800 and higher are excellent.

For credit scores that range from 300 to 850, a credit score in the mid to high 600s or above is generally considered good. A score in the high 700s or 800s is considered excellent. About a third of consumers have FICO® ScoresΘ that fall between 600 and 750—and an additional 48% have a higher score. In 2023, the average FICO® Score in the U.S. was 715.
Lenders use their own criteria for deciding whom to lend to and at what rates. But a higher credit score can generally help you qualify for a credit card or loan with a lower interest rate and better terms. The two main types of credit scores, the FICO® Score and VantageScore® credit scores, vary slightly in their ranges but have similar scoring factors.
Here's more on what qualifies as a good credit score, what impacts your credit and how to improve your credit scores.
What Is a Good FICO® Score?
The base FICO® Scores range from 300 to 850, and the good credit score range is 670 to 739.
FICO creates different types of consumer credit scores. There are "base" FICO® Scores that the company makes for lenders in multiple industries to use, as well as industry-specific credit scores for credit card issuers and auto lenders. FICO's industry-specific credit scores have a different range: 250 to 900. However, the middle categories have the same groupings, and a "good" industry-specific FICO® Score is still 670 to 739. Scores above that are considered very good or exceptional.
Learn more: What Is the Average Credit Score in the US?
What Is a Good VantageScore Credit Score?
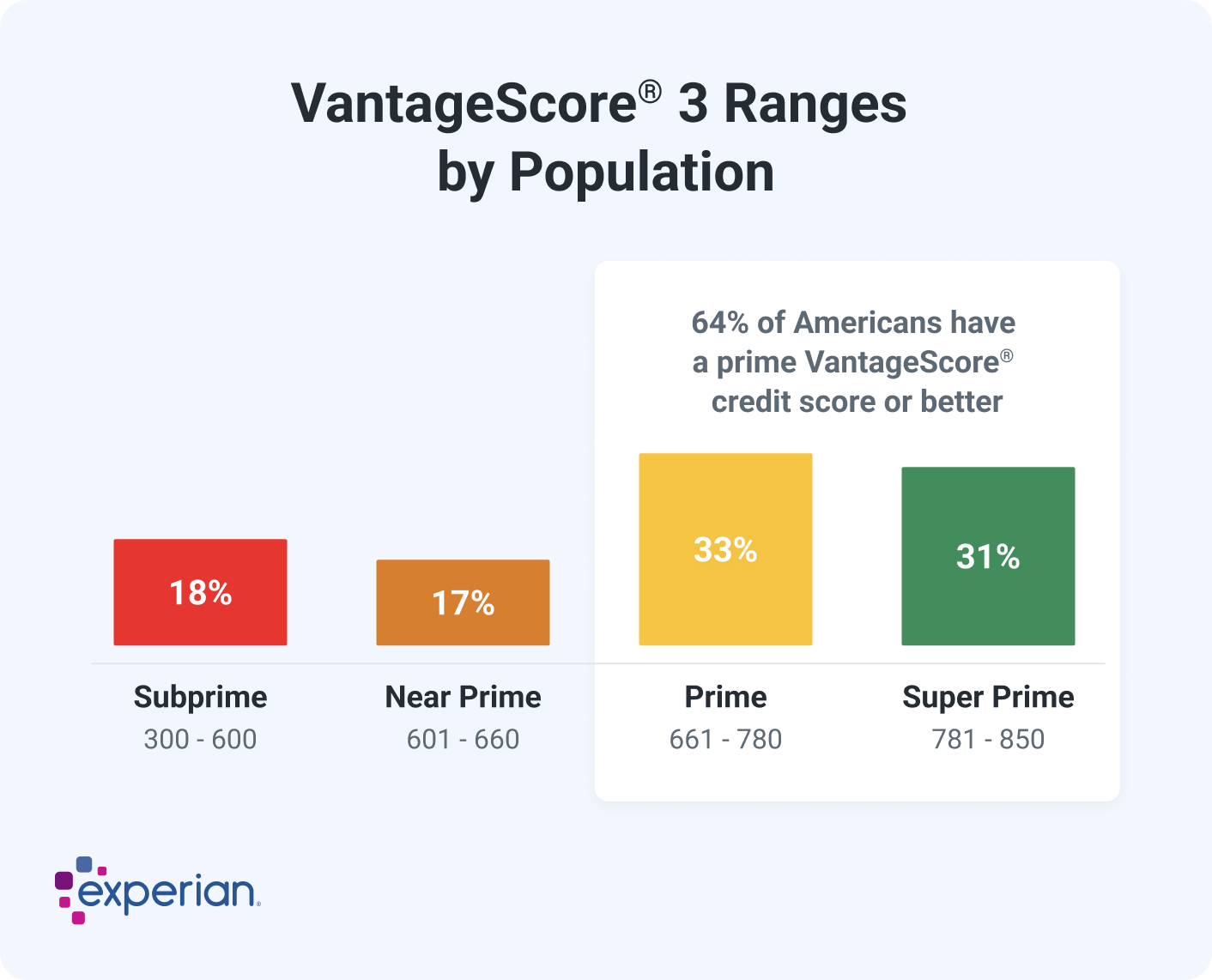
The latest VantageScore 3.0 and 4.0 credit scores use a range of 300 to 850—the same as the base FICO® Scores—and a good score is 661 to 780.
VantageScore doesn't have industry-specific credit scores, but it has released updated models over the years. The first two VantageScore credit scores had a 501 to 990 range, but lenders don't commonly use those scores.
What Affects Your Credit Scores?
The common factors that can affect all your credit scores fall into several categories:
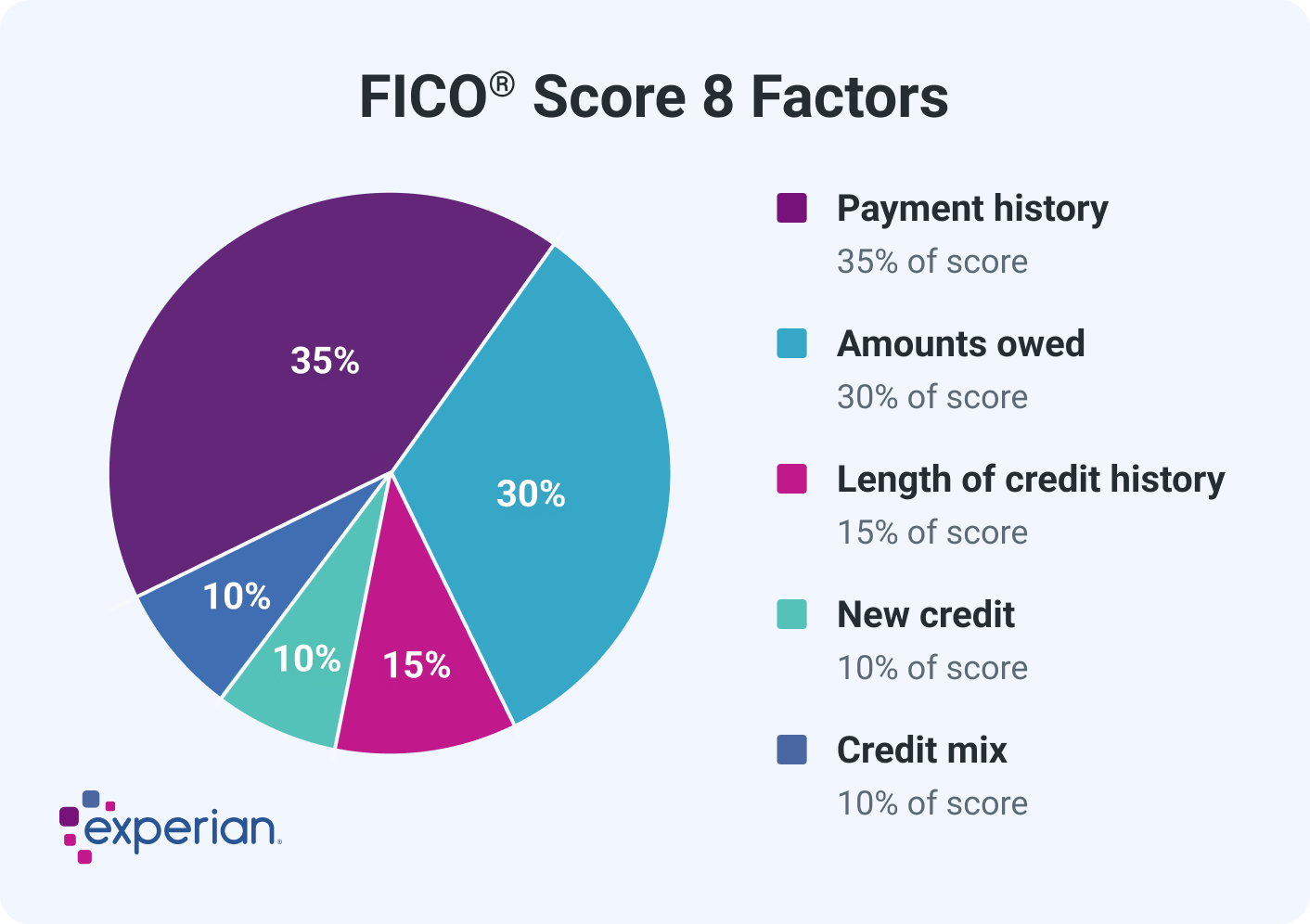
- Payment history: Making on-time payments on your credit accounts can help your scores. But missing payments, having an account sent to collections or filing bankruptcy could hurt your scores.
- Credit usage: How many of your accounts have balances, how much you owe and your credit utilization rate—the portion of your credit limit that you're using on revolving accounts such as credit cards—all come into play here.
- Length of credit history: This category includes the average age of all your credit accounts, along with the age of your oldest and newest accounts.
- Types of accounts: Also called "credit mix," this considers whether you're managing both installment accounts (such as a car loan, personal loan or mortgage) and revolving accounts (such as credit cards and other types of credit lines). Showing that you can manage both types of accounts responsibly generally helps your scores.
- Recent activity: This considers whether you've recently applied for or opened new accounts.
FICO and VantageScore take different approaches to explaining the relative importance of the categories.
Learn more: What Affects Your Credit Scores?
FICO® Score Factors
FICO uses percentages to represent how important each category generally is, but the exact percentage breakdown used to determine your credit score will depend on your unique credit report. FICO considers scoring factors in the following order:
VantageScore Credit Score Factors
VantageScore lists the factors by how influential they generally are in determining a credit score, but this will also depend on your unique credit report. VantageScore considers factors in the following order:
| VantageScore Credit Scoring Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Payment history | Extremely influential |
| Total credit usage | Highly influential |
| Credit mix and experience | Highly influential |
| New accounts opened | Moderately influential |
| Balances and available credit | Less influential |
What Information Credit Scores Do Not Consider
FICO and VantageScore do not consider the following information when calculating credit scores:
- Where you live: Including your current and previous addresses.
- Demographics and beliefs: Your age, race, color, religion, national origin, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity and marital status. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act prohibits creditors from considering this information, or using credit scores that consider this information, when making lending decisions.
- Income and employment: Your salary, occupation, title, employer, date employed or employment history. However, lenders may consider this information when making decisions.
- Soft inquiries: A record of when someone checks your credit for a non-lending purpose. Soft inquiries are often the result of companies reviewing existing customers' credit reports, creating marketing lists or responding to preapproval requests. They can also occur when you check your own credit report or when you use credit monitoring services from companies like Experian.
What Is a Good Credit Score to Buy a House?
To increase your odds of approval and qualify for a lower-rate mortgage, you should aim to have a credit score in the good range or higher. That's a FICO® Score of at least 670.
The minimum credit score you need to buy a house could range from around 500 to 700, but will ultimately depend on the type of mortgage loan you're applying for and your lender. Many lenders require a minimum credit score of 620 for a conventional mortgage. Other types of mortgages have different credit score requirements.
| Minimum Credit Score for Government-Backed Mortgages | |
|---|---|
| FHA home loans | 500 - 579 (10% down payment) 580+ (3.5% down payment) |
| USDA loans | 580 - 620 may be required by lenders, but there is no set minimum |
| VA loans | 620+ generally required by lenders |
Remember that your credit score plays an important role in determining the interest rate and payment terms on a mortgage loan. Lenders base the interest they charge on how risky they view you as a borrower. So while it may be possible to get a mortgage with bad credit, you're typically better off improving your score before you apply for a mortgage.
Learn more: Which Credit Scores Do Mortgage Lenders Use?
What Is a Good Credit Score to Buy a Car?
While there isn't a set minimum credit score to buy a car, a VantageScore credit score of 661 or higher could be a good score. You'll generally qualify for better auto loan terms as your score increases.
Auto lenders view low credit scores as a sign of risk, so an applicant with poor or fair credit will pay more in interest and might receive a lower loan limit. If you don't have a good score, try to improve your credit before you buy a car.
Learn more: Average Car Loan Interest Rates by Credit Score
Why There Are Different Credit Scores
There are many different credit scores because credit scoring companies continually update and sell their scores to lenders.
Lenders use credit scores to make lending and account management decisions, such as who to approve and whether to change your credit limit. For the most part, lenders can choose which model they want to use.
FICO and VantageScore create and sell different credit scoring models, and both companies periodically release new versions of their credit scores—similar to how a software company might offer a new operating system.
The latest scoring models might incorporate technological advances or changes in consumer behavior. Lenders can then decide to upgrade to a newer model, or to stick with the older version that's already integrated into their systems and processes.
Learn more: Why Are My Credit Scores Different?
VantageScore's Different Credit Scores
VantageScore creates a generic tri-bureau scoring model, meaning the score is designed for any type of lender. The same model can evaluate your credit reports from the three major consumer credit bureaus (Experian, TransUnion and Equifax).
VantageScore launched its first model—the VantageScore 1.0, which is no longer offered—in 2006. In 2017, it released VantageScore 4.0, which was the first generic credit score to use trended data, such as how your balances or credit utilization rate change over time.
VantageScore announced its VantageScore 4plus™ model in May 2024. Unlike previous versions, this model allows creditors to ask consumers if they would like to link a bank account and share their banking data. If the person links an account, VantageScore 4plus; can consider the banking data and recalculate their score.
| VS 3.0 | VS 4.0 | VS 4plus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Only considers data from a credit report | X | X | |
| Can consider additional data with your permission | X | ||
| Considers trended data | X | X |
FICO's Different Credit Scores
In 1989, FICO became the first company to create credit scoring models based on consumer credit reports. Although recent FICO® Score versions share a common name, such as FICO® Score 8, FICO creates different versions of the models for each credit bureau.
There are three general types of consumer FICO® Scores:
- Base FICO® Scores: These scores are created for any type of lender and they range from 300 to 850. The scores try to predict the likelihood that a consumer will fall behind on any type of credit obligation.
- Industry-specific FICO® Scores: FICO creates auto scores and bankcard scores specifically for auto lenders and card issuers. Industry scores aim to predict the likelihood that a consumer will fall behind on the specific type of account, and the scores range from 250 to 900.
- FICO® Scores that use alternative data: FICO has models that can incorporate alternative credit data, such as the UltraFICO® and FICO XD scores. Both scores range from 300 to 850. The former can consider linking deposit account information, and the latter can score people using nontraditional types of payment history from other databases, such as your telecom or utility payments.
FICO industry-specific scores are built on top of a base FICO® Score, and FICO periodically releases new suites of scores. For example, the FICO® Score 10 Suite includes a base FICO® Score 10, a FICO® Score 10 T (which considers trended data) and industry-specific scores.
Creditors Can Choose Which Credit Scores to Use
Lenders can choose which of your credit reports to request and which score, or scores, to receive. You often won't know which report or score the lender will use, and lenders might change their preferences or test different approaches.
The good news is most FICO and VantageScore credit scores rely on the same underlying information from one of your credit reports to determine your credit scores. They also all aim to make the same prediction—the likelihood that a person will become 90 days past due on a bill (either in general or a specific type) within the next 24 months.
As a result, the same factors can impact all your credit scores. If you monitor multiple credit scores, you could find that your scores vary depending on the scoring model and which one of your credit reports it analyzes. But, over time, you may see they all tend to rise and fall together.
Why Having a Good Credit Score Is Important
Having good credit can make achieving your goals easier. It could be the difference between qualifying or being denied for an important loan, such as a home mortgage or car loan. It can also directly impact how much you'll have to pay in interest or fees if you're approved.
For example, the difference between taking out a 30-year, fixed-rate $350,000 mortgage with a 620 FICO® Score and a 700 FICO® Score could be $138.58 a month. That's extra money you could be putting toward your savings or other financial goals. Over the lifetime of the loan, having the better score would save you $49,889 in interest payments.
Additionally, credit scores can impact non-lending decisions, such as whether a landlord will agree to rent you an apartment.
Your credit reports can also impact you in other ways. Some employers may review your credit reports (but not your credit scores) before making a hiring or promotion decision. In most states, insurance companies may use credit-based insurance scores to help determine your premiums for auto, home and life insurance.
| FICO® Score | Interest Rate, 30-Year Fixed-Rate Mortgage | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 620 | 7.71% | $2,806.11 | $549,199 |
| 700 | 7.13% | $2,667.53 | $499,310 |
| 840 | 6.69% | $2,564.49 | $462,214 |
Source: Curinos LLC, December 6, 2024; assumes a $350,000 mortgage and 30-day rate-lock period
Learn more: Facts About Credit You May Not Know
How to Improve Your Credit Scores
To improve your credit, focus on the underlying factors that affect your scores. At a high level, the basic steps you need to take are fairly straightforward:
- Make at least your minimum payment on time. Even a single payment that's 30 days past due can hurt your credit scores, and the late payment will stay on your credit report for up to seven years. If you think you may miss a payment, reach out to your creditors as quickly as possible to see if they can work with you and help you stay in good standing.
- Keep your credit card balances low. Your credit utilization rate is an important scoring factor that compares the balances and credit limits of revolving accounts, such as credit cards, from your credit report. A low credit utilization rate can help your credit scores, and people with excellent credit scores tend to have an overall utilization rate in the single digits.
- Open accounts that will be reported to the credit bureaus. Having several open and active credit accounts can thicken your credit file and make qualifying for credit easier. A mix of open installment and revolving accounts can also improve your scores.
- Only apply for credit when you need it. Applying for a new account can lead to a hard inquiry, which may hurt your credit scores a little. The impact is often minimal, but applying for many different types of loans or credit cards during a short period could lead to a larger score drop.
- Review your credit reports regularly. Look over each of your three credit reports for inaccuracies or fraudulent accounts that might be hurting your credit scores; for example, an account that's incorrectly reported as past due or a credit card with a high balance that you didn't open. You have the right to dispute errors and have the creditor or credit bureau investigate.
Other factors can also impact your scores. For example, increasing the average age of your accounts could help your scores. However, that's often a matter of waiting for existing credit accounts to age rather than taking action.
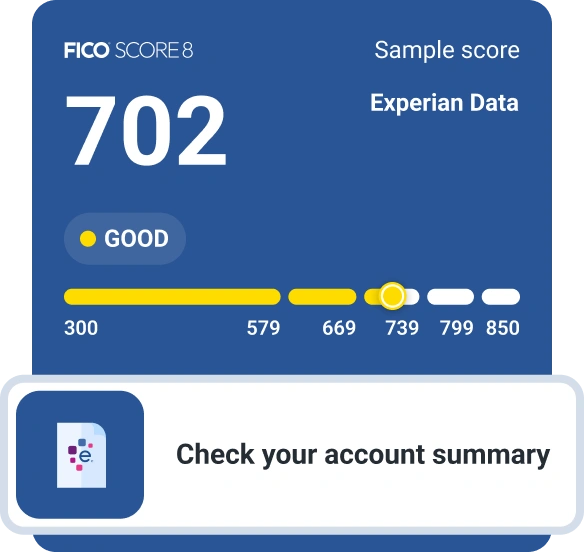
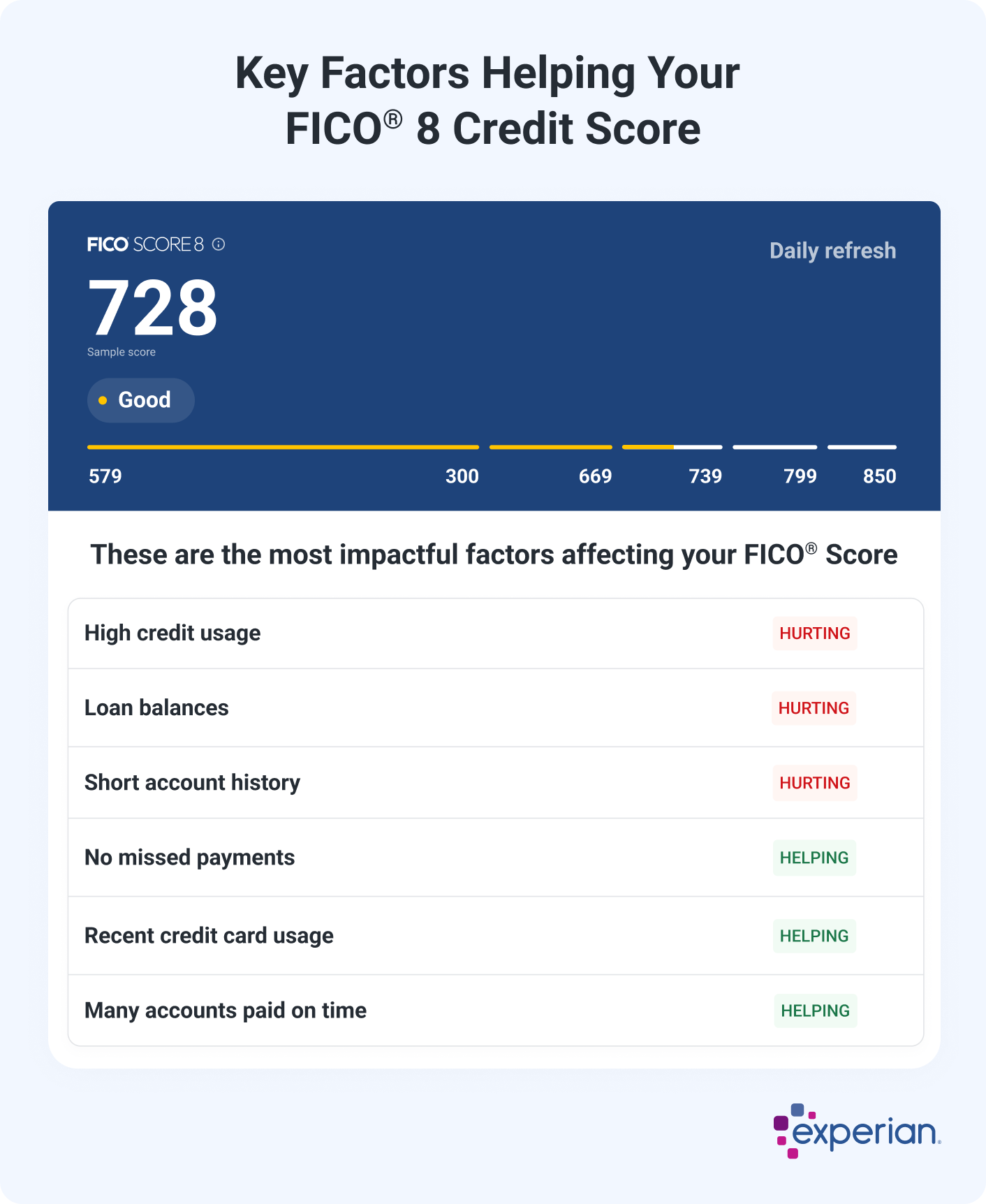
Checking your credit scores might also give you insight into what you can do to improve them. For example, when you check your FICO® Score 8 from Experian for free, you can get an overview of how lenders see you based on your credit:

You'll also get an overview of your score profile, with an explanation of what's helping and hurting your score the most.
What to Do if You Don't Have a Credit Score
Credit scoring models can't score credit reports that don't have enough information.
For FICO® Scores, you need:
- An account that's at least six months old
- An account that has been active in the past six months
VantageScore can score your credit report if it has at least one active account, even if the account is only a month old.
If you aren't scoreable, you can:
- Sign up for Experian Go™. Experian Go helps you jump-start your credit by creating an Experian credit report for you even if you don't have any credit accounts yet. It then provides you with personalized insights on how to move forward with building credit.
- Use Experian Boost®ø. Once you have an Experian credit report, you can use Experian Boost to get credit for certain qualifying bills, such as utility bills, streaming subscriptions, insurance and eligible rent payments. These payments can be added to your credit history and instantly increase your FICO® Score.
- Become an authorized user. When someone adds you as an authorized user on one of their credit cards, the account's details and history might be added to your credit report. It can help you establish your credit, although the account could also help or hurt your score depending on how the primary cardholder manages the card.
- Open new credit accounts. It can be difficult to qualify for new credit accounts when you don't already have a credit score. But there may be some low- and no-fee options, such as credit-builder loans, lending circles and secured credit cards that don't have an annual fee.
Learn more: Ways to Build Credit if You Have No Credit History
Why Your Credit Score Changed
Your credit score can change for many reasons, and it's not uncommon for scores to move up or down throughout the month as new information gets added to your credit reports.
Your credit scores might increase if:
- Negative items fall off your credit report
- You lower your credit utilization rate
- You pay off or settle collection accounts
- You add new on-time payments to your credit report
Your credit scores might decrease if:
- A credit card or loan payment becomes 30 days past due
- Your credit utilization rate increases
- You apply for or open a new credit account
- You file for bankruptcy
Some actions might have an unexpected impact on your credit scores. Paying off a loan, for example, could lead to a score drop even though it's a positive action in terms of responsible money management. This could be because it was the only open installment account you had on your credit report or the only loan with a low balance. After paying off the loan, you may be left without a mix of open installment and revolving accounts, or with only high-balance loans, which could have a negative effect.
Additionally, credit scoring models use complicated calculations to determine a score. A single event isn't "worth" a certain amount of points—the change will depend on your entire credit report.
For example, a late payment could lead to a large point drop for someone who's never missed a payment because it may indicate a change in their behavior or financial position. However, someone who has already missed many payments might experience a smaller point drop from a new late payment because it's assumed that they're more likely to miss payments.
Monitor Your Credit Report and Score
Checking your credit score right before you apply for a new loan or credit card can help you understand your chances of getting approved and qualifying for favorable terms. But regularly checking it further ahead of time gives you the chance to improve your scores, and possibly save hundreds or thousands of dollars in interest.
You can check and monitor your FICO® Score and credit report for free from Experian with daily updates and real-time alerts for suspicious changes in your report. A free account also offers free credit-building features, like Experian Boost, and insights into your credit history and score.
What makes a good credit score?
Learn what it takes to achieve a good credit score. Review your FICO® Score for free and see what’s helping and hurting your score.
Get your FICO® ScoreNo credit card required
About the author
Louis DeNicola is freelance personal finance and credit writer who works with Fortune 500 financial services firms, FinTech startups, and non-profits to teach people about money and credit. His clients include BlueVine, Discover, LendingTree, Money Management International, U.S News and Wirecutter.
Read more from Louis